'Network'에 해당되는 글 204건
- 2009.02.03 필요하면 어디서든 선언해 놓아야 한다... ns2 WLAN
- 2009.02.03 DIFS제어 방법 ns2
- 2009.02.03 NS2에서 802_11의 재전송 수 포기에 따른 카운터를 세고 싶을 때
- 2009.02.03 ns2 코드에서 재전송 수를 직접 제어할 때!
- 2009.02.03 지금까지 실험한 결과들의 엑셀 파일
- 2009.02.02 WLAN에서 업스트림과 다운스트림의 시뮬레이션을 위한 강좌
- 2009.01.28 ns2 모듈 및 변수 함수 설명
- 2009.01.21 Node 30개인 경우 CWmin 8 CWmax8의 결과와 재전송의 변화에 따른 결과
- 2009.01.18 ENUM
- 2009.01.18 실시간 통신 시스템 위한 VoIP 표준 프로토콜 H.323과 ..
double up_sum,down_sum;
struct hdr_cmn *ch = HDR_CMN(p);//패킷 정보
struct hdr_mac802_11* dh = HDR_MAC802_11(p);//맥 정보
struct hdr_ip *iph =HDR_IP(p); //ip 정보
//접근자에 정보를 직접 수정할 수 있게 만들어 나가는 작업은 힘들다..
해당 단말만 되는것인지에 대한 신뢰를 하기도 힘들다.
하지만 항상 디테일한 테스트 범위를 구성해 나가면 이러한 문제는 시간이
해결해 준다.
int src = Address::instance().get_nodeaddr(iph->saddr());
int dst1 = Address::instance().get_nodeaddr(iph->daddr());
int sport = Address::instance().get_nodeaddr(iph->sport());
int dport = Address::instance().get_nodeaddr(iph->dport());
int seq=dh2->seqno();
char *check_name = (char *)packet_info.name(ch->ptype()); //패킷 종류
double now = Scheduler::instance().clock();
//시뮬레이션 시간 가져온다 알뜰 살뜰 참 다양하게 썼다.
'Network > Simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 모니터링 시스템 구현을 위한 동작 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
|---|---|
| 재전송 수를 구간별로 적용시키기 위해 NS2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| DIFS제어 방법 ns2 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| NS2에서 802_11의 재전송 수 포기에 따른 카운터를 세고 싶을 때 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| ns2 코드에서 재전송 수를 직접 제어할 때! (0) | 2009.02.03 |
802_11헤더의 class PHY_MIB를 확인하면
getDIFS()가 있다. 나는 AP의 DIFS만을 변경해주기 위해
해당 함수를 하나더 만들었다.
SIFSTime은 10마이크로 세컨드..
슬롯타임은 20마이크로 세컨드..
DIFS는 슬롯타임 * 2 + SIFS 시간이다. 즉 50마이크로 세컨드....
테스트 할 때는 그냥 수작업하였지만..
모니터링을 만들기 위해 파라미터를 선언했다. APDIFS 더블형으로..
초기화 할때 같이 밀어넣어준다. 일단 초기값으로..
문제는...
cc파일 안의 내용이다.
getDIFS()호출부를 그대로 찾아서..
add() 결과시 0 즉 AP이면 GETDIFS1()를 호출하고 아니면 일반적인 함수를
호출하도록 만들었다.
귀찮다 ㅡㅡㅋ
'Network > Simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 재전송 수를 구간별로 적용시키기 위해 NS2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
|---|---|
| 필요하면 어디서든 선언해 놓아야 한다... ns2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| NS2에서 802_11의 재전송 수 포기에 따른 카운터를 세고 싶을 때 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| ns2 코드에서 재전송 수를 직접 제어할 때! (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| 지금까지 실험한 결과들의 엑셀 파일 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
retransmitRTS()
retransmitDATA()
구문을 읽다보면 retrylimit나 쓰레숄더 값과 비교하는 구문이 있다.
디스카드 하기 전에 입력한다.
double now = Scheduler::instance().clock();
if(200.0 <= now)
{
if(addr()==0)
{
AP++;
printf("%lf AP : %d\n",now,AP);
}
else
{
client++;
printf("%lf client : %d client number %d\n",now,addr(),client);
}
}
헤더파일에 802 클래스를 찾아서
퍼블릭 선언부에 AP와 client를 선언하고
cc파일에서 초기화 할때 같이 0으로 선언해 줄 수 있도록 하자.
'Network > Simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 필요하면 어디서든 선언해 놓아야 한다... ns2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
|---|---|
| DIFS제어 방법 ns2 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| ns2 코드에서 재전송 수를 직접 제어할 때! (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| 지금까지 실험한 결과들의 엑셀 파일 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| WLAN에서 업스트림과 다운스트림의 시뮬레이션을 위한 강좌 (0) | 2009.02.02 |
public 선언부에
u_int32_t CWMin;
u_int32_t CWMax;
각각 선언한다. 물론 다른 위치에 존재하는 동일 선언자는 삭제하거나 주석처리..
send() 함수에 아래와 같이 구현한다.
화면이 미치도록 올라가는 것을 확인할 수 있다
참고로 AP는 Node 넘버가 0번이다. 훗..
if(addr()==0)
{
phymib_.CWMin=7;
phymib_.CWMax=7;
}
printf("\nnode number= %d cwmin= %d cwmax= %d ",addr(),phymib_.CWMin,phymib_.CWMax);
'Network > Simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 필요하면 어디서든 선언해 놓아야 한다... ns2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
|---|---|
| DIFS제어 방법 ns2 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| NS2에서 802_11의 재전송 수 포기에 따른 카운터를 세고 싶을 때 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| 지금까지 실험한 결과들의 엑셀 파일 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| WLAN에서 업스트림과 다운스트림의 시뮬레이션을 위한 강좌 (0) | 2009.02.02 |
'Network > Simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 필요하면 어디서든 선언해 놓아야 한다... ns2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
|---|---|
| DIFS제어 방법 ns2 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| NS2에서 802_11의 재전송 수 포기에 따른 카운터를 세고 싶을 때 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| ns2 코드에서 재전송 수를 직접 제어할 때! (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| WLAN에서 업스트림과 다운스트림의 시뮬레이션을 위한 강좌 (0) | 2009.02.02 |
여태 만든것이 다 날라가고...
새로이 실험으로 증빙된 올바른 소스와 정보만을 올리기로 한다.
NS2 실험을 위한 과정..
NS2는 본래 trace 파일을 가지고 원하는 데이터를 추출하기 위해 여러 동작을 하게 된다.
이러한 동작에 있어서 많은 노동의 고통이 따르기 때문에 나는 up_down_stream2.sh라는 쉘 스크립트 파일을 만들어 사용하였다.
아래는 up_down-stream2.sh 파일 내용이다.
###########################################################################
#!/bin/sh
echo "Awk ShellScript"
num=1
num1=1
num2=1
rm -rf *~ *.*~ data/check_retry_*~ data/buffer_50_up_down_th_*~ data/drop_*~ data/check_retry_* data/buffer_50_up_down_th_* data/drop_* *.tr
#한번 생성한 파일위로 다시 실험한 데이터가 쌓이면 매우 피곤하다. 이에 삭제를 먼저 하고 실행할 수 있도록 만들었다.
for Tcl_file in 40 #노드 수
do
for Tcl_file1 in 7 #CWmin
do
for Tcl_file2 in 7 #CWmax
do
echo "###################### TCL" $num "\t "$Tcl_file
ns data$Tcl_file.tcl $Tcl_file1 $Tcl_file2 > data/check_retry_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$Tcl_file2
num=`expr $num + 1` #나는 MAC에서 재전송 포기에 의한 패킷 수를 세기위한 소스를 만들어 따로 trace파일을 만들 필요가 있었다. 다른 살마들은 안해도 되며, 실행 위치의 data 폴더에 저장되도록 만들었다.
done
done
done
for Tcl_file in 40
do
for Tcl_file1 in 7
do
for PacketSize in 7
do
echo "###################### TCL_Mobile_change" $num1
echo "awk -f awk-ack_rec_wire up_down_stream_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize.tr >> testbook"
sed 's/_/ /' up_down_stream_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize.tr > testbook
sed 's/_/ /' testbook > up_down_stream_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize.tr
rm -rf testbook
#아주 중요한 구문이다. trace 파일의 무선 노드의 식별 넘버에는 양쪽에 언더바가 생성된다.
이 언더바를 지우는 과정이다.
num1=`expr $num1 + 1`
done
done
done
for Tcl_file in 40
do
for Tcl_file1 in 7
do
for PacketSize in 7
do
echo "###################### Throughput" $num2
echo "awk -f awk-throughput -v nn=$PacketSize up_down_stream_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize.tr >> up_down_Th"
awk -f drop nn=$Tcl_file nn1=$Tcl_file1 nn2=$PacketSize up_down_stream_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize.tr >> data/drop_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize
awk -f awk-throughput nn=$Tcl_file nn1=$Tcl_file1 nn2=$PacketSize #드롭률 data 폴더의 해당 이름으로 생성시킨다.
up_down_stream_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize.tr >> data/buffer_50_up_down_th_$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file-$Tcl_file1-$PacketSize#처리량을 data폴더의 해당 이름으로 생성 시킨다.
done
done
done
###########################################################################
위의 실험에 있어서
trace 파일은 drop이란 awk 스크립트 파일을 호출하여 재 필터링 된다.
##########################################################################
BEGIN {
sum1=0;
sum2=0;
sum3=0;
sum4=0;
}
{
if(200<$2)#500초의 실험 시간 중 200초의 안정화 시간을 기다린후 이후값만 측정한다.
{
if (($1 == "D")&&($4 =="IFQ")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($5!="END")&&($3 == (nn+1))) {
sum1++;
} #nn은 외부 입력 값이다. 쉘 스크립트를 확인하면 된다.
if (($1 == "D")&&($4 =="IFQ")&&($7=="ack" )&&($5!="END")&&($3 == (nn+1))) {
sum2++;
}
if (($1 == "D")&&($4 =="IFQ")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($5!="END")&&($3 != (nn+1))) {
sum3++;
}
if (($1 == "D")&&($4 =="IFQ")&&($7=="ack" )&&($5!="END")&&($3 != (nn+1))) {
sum4++;
}
}
}
END {
print (nn+1);
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2," AP_ACK drop number : ",sum2,"\t","AP_DATA drop number : ",sum1
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2," CLI_ACK drop number : ",sum4,"\t","CLI_DATA drop number : ",sum3,"\n"
}
##########################################################################
drop을 필터링 하고 나면
총 처리량과 공평성 상태를 측정해야 한다.
처리량은 먼저 업스트림과 다운스트림을 측정한뒤 나머지를 산출한다.
awk-throughput이란 파일 명으로 생성된다.
##########################################################################
BEGIN {
total_byte1=0;
total_byte_th1=0;
first_time1=0;
last_time1=0;
total_byte2=0;
total_byte_th2=0;
first_time2=0;
last_time2=0;
sum1=0;
sum2=0;
node = $3;
}
{
if(200<$2)
{
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 != nn)&&($4 != (nn+1))) {
if(first_time1=="0") first_time1=$2;
last_time1=$2;
total_byte1 += $6;
sum1++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 != (nn+1))) {
if(first_time2=="0") first_time2=$2;
last_time2=$2;
total_byte2 += $8;
sum2++;
}
}
}
END {
fairness_index=total_byte1/total_byte2
total=total_byte1+total_byte2
# fairness_index=sum1/sum2
# print "fairness index = ",fairness_index, "time 1 = ", last_time1,"time 2 = ",last_time2;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte1\t",((total_byte1*8/300)/1000000) ,"\t down: total_byte2\t",((total_byte2*8/300)/1000000) ,"\tfairness_index: ",fairness_index,"\t","total = ",((total*8/300)/1000000);
}
############################################################################
혹시나 플로우별 처리량이 필요하다면.....
10개 단위시(필요한 파일명으로 저장하면 된다)
사용방법은 쉘 스크립트 참조
###########################################################################
BEGIN {
}
{
if(200<$2)
{
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 0)) {
total_byte0 += $6;
sum0++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 1)) {
total_byte1 += $6;
sum1++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 2)) {
total_byte2 += $6;
sum2++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 3)) {
total_byte3 += $6;
sum3++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 4)) {
total_byte4 += $6;
sum4++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 5)) {
total_byte5 += $6;
sum5++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 6)) {
total_byte6 += $6;
sum6++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 7)) {
total_byte7 += $6;
sum7++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 8)) {
total_byte8 += $6;
sum8++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 9)) {
total_byte9 += $6;
sum9++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==12 )) {
total_byte12 += $8;
sum12++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==13 )) {
total_byte13 += $8;
sum13++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==14 )) {
total_byte14 += $8;
sum14++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==15 )) {
total_byte15 += $8;
sum15++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==16 )) {
total_byte16 += $8;
sum16++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==17 )) {
total_byte17 += $8;
sum17++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==18 )) {
total_byte18 += $8;
sum18++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==19 )) {
total_byte19 += $8;
sum19++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==20 )) {
total_byte20 += $8;
sum20++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==21 )) {
total_byte21 += $8;
sum21++;
}
}
}
END {
fairness_index=total_byte1/total_byte2
total=total_byte1+total_byte2
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte0*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum0;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte1*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum1;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte2*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum2;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte3*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum3;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte4*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum4;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte5*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum5;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte6*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum6;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte7*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum7;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte8*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum8;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte9*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum9,"\n";
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte12*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum12;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte13*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum13;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte14*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum14;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte15*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum15;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte16*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum16;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte17*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum17;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte18*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum18;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte19*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum19;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte20*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum20;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte21*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum21;
}
##########################################################################
30개의 노드일 때 플로우별 처리량
##########################################################################
BEGIN {
}
{
if(200<$2)
{
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 0)) {
total_byte0 += $6;
sum0++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 1)) {
total_byte1 += $6;
sum1++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 2)) {
total_byte2 += $6;
sum2++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 3)) {
total_byte3 += $6;
sum3++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 4)) {
total_byte4 += $6;
sum4++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 5)) {
total_byte5 += $6;
sum5++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 6)) {
total_byte6 += $6;
sum6++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 7)) {
total_byte7 += $6;
sum7++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 8)) {
total_byte8 += $6;
sum8++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 9)) {
total_byte9 += $6;
sum9++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 10)) {
total_byte10 += $6;
sum10++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 11)) {
total_byte11 += $6;
sum11++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 12)) {
total_byte12 += $6;
sum12++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 13)) {
total_byte13 += $6;
sum13++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 14)) {
total_byte14 += $6;
sum14++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 15)) {
total_byte15 += $6;
sum15++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 16)) {
total_byte16 += $6;
sum16++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 17)) {
total_byte17 += $6;
sum17++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 18)) {
total_byte18 += $6;
sum18++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 19)) {
total_byte19 += $6;
sum19++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 20)) {
total_byte20 += $6;
sum20++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 21)) {
total_byte21 += $6;
sum21++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 22)) {
total_byte22 += $6;
sum22++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 23)) {
total_byte23 += $6;
sum23++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 24)) {
total_byte24 += $6;
sum24++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 25)) {
total_byte25 += $6;
sum25++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 26)) {
total_byte26 += $6;
sum26++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 27)) {
total_byte27 += $6;
sum27++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 28)) {
total_byte28 += $6;
sum28++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($5 =="tcp")&&($4 == 29)) {
total_byte29 += $6;
sum29++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 32)) {
total_byte32 += $8;
sum32++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==33)) {
total_byte33 += $8;
sum33++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 34)) {
total_byte34 += $8;
sum34++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==35)) {
total_byte35 += $8;
sum35++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 36)) {
total_byte36 += $8;
sum36++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==37)) {
total_byte37 += $8;
sum37++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==38)) {
total_byte38 += $8;
sum38++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 39)) {
total_byte39 += $8;
sum39++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 40)) {
total_byte40 += $8;
sum40++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==41 )) {
total_byte41 += $8;
sum41++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 42)) {
total_byte42 += $8;
sum42++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==43)) {
total_byte43+= $8;
sum43++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 44)) {
total_byte44 += $8;
sum44++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==45 )) {
total_byte45 += $8;
sum45++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==46)) {
total_byte46 += $8;
sum46++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==47 )) {
total_byte47 += $8;
sum47++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==48 )) {
total_byte48 += $8;
sum48++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==49 )) {
total_byte49 += $8;
sum49++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 50)) {
total_byte50 += $8;
sum50++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==51 )) {
total_byte51 += $8;
sum51++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 52)) {
total_byte52 += $8;
sum52++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==53 )) {
total_byte53 += $8;
sum53++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==54 )) {
total_byte54 += $8;
sum54++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==55 )) {
total_byte55 += $8;
sum55++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==56 )) {
total_byte56 += $8;
sum56++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==57 )) {
total_byte57 += $8;
sum57++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 == 58)) {
total_byte58 += $8;
sum58++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==59 )) {
total_byte59 += $8;
sum59++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==60 )) {
total_byte60 += $8;
sum60++;
}
if ( ($1 == "r")&&($4 =="AGT")&&($7=="tcp" )&&($3 ==61 )) {
total_byte61 += $8;
sum61++;
}
}
}
END {
fairness_index=total_byte1/total_byte2
total=total_byte1+total_byte2
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte0*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum0;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte1*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum1;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte2*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum2;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte3*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum3;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte4*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum4;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte5*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum5;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte6*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum6;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte7*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum7;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte8*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum8;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte9*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum9;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte10*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum10;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte11*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum11;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte12*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum12;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte13*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum13;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte14*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum14;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte15*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum15;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte16*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum16;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte17*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum17;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte18*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum18;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte19*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum19;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte20*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum20;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte21*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum21;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte22*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum22;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte23*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum23;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte24*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum24;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte25*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum25;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte26*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum26;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte27*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum27;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte28*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum28;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","up: total_byte\t", ((total_byte29*8/300)/1000000),"up: NUM\t", sum29,"\n";
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte32*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum32;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte33*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum33;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte34*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum34;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte35*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum35;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte36*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum36;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte37*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum37;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte38*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum38;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte39*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum39;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte40*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum40;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte41*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum41;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte42*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum42;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte43*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum43;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte44*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum44;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte45*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum45;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte46*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum46;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte47*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum47;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte48*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum48;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte49*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum49;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte50*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum50;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte51*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum51;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte52*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum52;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte53*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum53;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte54*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum54;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte55*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum55;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte56*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum56;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte57*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum57;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte58*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum58;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte59*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum59;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte60*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum60;
print nn,":",nn,"_",nn1,"_",nn2,"\t","down: total_byte\t", ((total_byte61*8/300)/1000000),"down: NUM\t", sum61;
}
###########################################################################
30개 노드에 대한 tcl소스이다.
데이터 명은 data30.tcl이다.
###########################################################################
### This simulation is an example of combination of wired and wireless
### topologies.
global opt
set opt(chan) Channel/WirelessChannel
set opt(prop) Propagation/TwoRayGround
set opt(netif) Phy/WirelessPhy
set opt(mac) Mac/802_11
set opt(ifq) Queue/DropTail/PriQueue
set opt(ll) LL
set opt(ant) Antenna/OmniAntenna
set opt(x) 500
set opt(y) 500
set opt(ifqlen) 50
set opt(adhocRouting) DSDV;#AODV ;#DSDV, DSR
set opt(cp) ""
set opt(sc) "../mobility/scene/scen-3-test"
set opt(stop) 500
set num_wired_nodes 2
set num_bs_nodes 1
set opt(mn) 30 #노드 총 개수이다.
set cmin [lindex $argv 0]
set cmax [lindex $argv 1]
set opt(nm) 31 #AP 혹은 라우터를 포함한 개수
Agent/TCP set packetSize_ 1480
# Mac/802_11 set RTSThreshold_ 99999 #RTS CTS 사용 안할시 주석처리 풀어준다.
Mac/802_11 set dataRate_ 11.0e6 ;# 11Mbps
Mac/802_11 set basicRate_ 11.0e6 ;# 1Mbps
# ===========================================================
# 802.11b value
#The Antenna height of transmitter and receiver is 1.5m.
Phy/WirelessPhy set bandwidth_ 11Mb
#===============================================================
set ns_ [new Simulator]
# set up for hierarchical routing
$ns_ node-config -addressType hierarchical
AddrParams set domain_num_ 2 ;# number of domains
lappend cluster_num 1 1 ;# number of clusters in each domain
AddrParams set cluster_num_ $cluster_num
lappend eilastlevel $opt(nm) $opt(nm) ;# number of nodes in each cluster
AddrParams set nodes_num_ $eilastlevel ;# of each domain
set tracefd [open up_down_stream_$opt(mn)-$opt(mn)-$cmin-$cmax.tr w]
$ns_ trace-all $tracefd
# Create topography object
set topo [new Topography]
# define topology
$topo load_flatgrid $opt(x) $opt(y)
# create God
create-god $opt(nm)
set temp {0.0.0 0.0.1 0.0.2 0.0.3 0.0.4 0.0.5 0.0.6 0.0.7 0.0.8 0.0.9 0.0.10 0.0.11 0.0.12 0.0.13 0.0.14 0.0.15 0.0.16 0.0.17 0.0.18 0.0.19 0.0.20 0.0.21 0.0.22 0.0.23 0.0.24 0.0.25 0.0.26 0.0.27 0.0.28 0.0.29 0.0.30 0.0.31 0.0.32 0.0.33 0.0.34 0.0.35 0.0.36 0.0.37 0.0.38 0.0.39 0.0.40 0.0.41 0.0.42 0.0.43 0.0.44 0.0.45 0.0.46 0.0.47 0.0.48 0.0.49 0.0.50 0.0.51 0.0.52 0.0.53 0.0.54 0.0.55 0.0.56 0.0.57 0.0.58 0.0.59 0.0.60 0.0.61 0.0.62 0.0.63 0.0.64 0.0.65 0.0.66 0.0.67 0.0.68 0.0.69 0.0.70 0.0.71 0.0.72 0.0.73 0.0.74 0.0.75 0.0.76 0.0.77 0.0.78 0.0.79 0.0.80} ;# hierarchical addresses for wired domain
for {set i 0} {$i < $opt(nm)} {incr i} {
set W($i) [$ns_ node [lindex $temp $i]]
}
Mac/802_11 set CWMin_ $cmin
Mac/802_11 set CWMax_ $cmax
#Mac/802_11 set ShortRetryLimit_ 7 ;# retransmittions
#Mac/802_11 set LongRetryLimit_ 4 ;# retransmissions
#재전송 수 제한을 풀어줄 때는 주석처리 제거 후 조절
$ns_ node-config -adhocRouting $opt(adhocRouting) \
-llType $opt(ll) \
-macType $opt(mac) \
-ifqType $opt(ifq) \
-ifqLen $opt(ifqlen) \
-antType $opt(ant) \
-propType $opt(prop) \
-phyType $opt(netif) \
-channelType $opt(chan) \
-topoInstance $topo \
-wiredRouting ON \
-agentTrace ON \
-routerTrace OFF \
-macTrace OFF \
set temp {1.0.0 1.0.1 1.0.2 1.0.3 1.0.4 1.0.5 1.0.6 1.0.7 1.0.8 1.0.9 1.0.10 1.0.11 1.0.12 1.0.13 1.0.14 1.0.15 1.0.16 1.0.17 1.0.18 1.0.19 1.0.20 1.0.21 1.0.22 1.0.23 1.0.24 1.0.25 1.0.26 1.0.27 1.0.28 1.0.29 1.0.30 1.0.31 1.0.32 1.0.33 1.0.34 1.0.35 1.0.36 1.0.37 1.0.38 1.0.39 1.0.40 1.0.41 1.0.42 1.0.43 1.0.44 1.0.45 1.0.46 1.0.47 1.0.48 1.0.49 1.0.50 1.0.51 1.0.52 1.0.53 1.0.54 1.0.55 1.0.56 1.0.57 1.0.58 1.0.59 1.0.60 1.0.61 1.0.62 1.0.63 1.0.64 1.0.65 1.0.66 1.0.67 1.0.68 1.0.69 1.0.70 1.0.71 1.0.72 1.0.73 1.0.74 1.0.75 1.0.76 1.0.77 1.0.78 1.0.79 1.0.80} ;# hier address to be used for wireless
set BS(0) [$ns_ node [lindex $temp 0]]
$BS(0) random-motion 0
#무선 AP에만 특정한 CWmin과 CWmax만을 적용해야 했으므로 무선 단말기 선언시에는 새로운 정보를 입력후 무선 환경을 재설정 한다.
Mac/802_11 set CWMin_ 31
Mac/802_11 set CWMax_ 1023
# Mac/802_11 set ShortRetryLimit_ 7 ;# retransmittions
# Mac/802_11 set LongRetryLimit_ 4 ;# retransmissions
$ns_ node-config -adhocRouting $opt(adhocRouting) \
-llType $opt(ll) \
-macType $opt(mac) \
-ifqType $opt(ifq) \
-ifqLen $opt(ifqlen) \
-antType $opt(ant) \
-propType $opt(prop) \
-phyType $opt(netif) \
-channelType $opt(chan) \
-topoInstance $topo \
-wiredRouting ON \
-agentTrace ON \
-routerTrace OFF \
-macTrace OFF \
for {set j 0} {$j < $opt(mn)} {incr j} {
set node_($j) [ $ns_ node [lindex $temp \
[expr $j+1]] ]
$node_($j) base-station [AddrParams addr2id [$BS(0) node-addr]]
}
$ns_ duplex-link $W(0) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(1) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(2) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(3) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(4) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(5) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(6) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(7) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(8) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(9) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(10) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(11) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(12) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(13) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(14) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(15) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(16) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(17) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(18) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(19) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(20) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(21) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(22) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(23) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(24) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(25) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(26) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(27) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(28) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(29) $W(30) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(30) $BS(0) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
#중요한 내용... 각 라우터와 AP간의 전파 딜레이가 너무 짧으면 세그먼트 에러 출력될 가능성이 높다. 이유는 그냥 추측만.... 또한 for문을 사용하여 스크립트 작성시 세그먼트 에러 출력될 가능성이 높다. 물론 문제없이 작성하더라도 말이다. 이유는 전혀 모르겠다. ㅎ
#===============================================================
#down strem for TCP
set tcp_(0) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(0) set class_ 2
set sink_(0) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(0) $tcp_(0)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(0) $sink_(0)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(0) $sink_(0)
set ftp_(0) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(0) attach-agent $tcp_(0)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(0) start"
set tcp_(1) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(1) set class_ 2
set sink_(1) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(1) $tcp_(1)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(1) $sink_(1)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(1) $sink_(1)
set ftp_(1) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(1) attach-agent $tcp_(1)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(1) start"
set tcp_(2) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(2) set class_ 2
set sink_(2) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(2) $tcp_(2)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(2) $sink_(2)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(2) $sink_(2)
set ftp_(2) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(2) attach-agent $tcp_(2)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(2) start"
set tcp_(3) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(3) set class_ 2
set sink_(3) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(3) $tcp_(3)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(3) $sink_(3)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(3) $sink_(3)
set ftp_(3) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(3) attach-agent $tcp_(3)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(3) start"
set tcp_(4) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(4) set class_ 2
set sink_(4) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(4) $tcp_(4)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(4) $sink_(4)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(4) $sink_(4)
set ftp_(4) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(4) attach-agent $tcp_(4)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(4) start"
set tcp_(5) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(5) set class_ 2
set sink_(5) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(5) $tcp_(5)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(5) $sink_(5)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(5) $sink_(5)
set ftp_(5) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(5) attach-agent $tcp_(5)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(5) start"
set tcp_(6) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(6) set class_ 2
set sink_(6) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(6) $tcp_(6)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(6) $sink_(6)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(6) $sink_(6)
set ftp_(6) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(6) attach-agent $tcp_(6)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(6) start"
set tcp_(7) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(7) set class_ 2
set sink_(7) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(7) $tcp_(7)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(7) $sink_(7)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(7) $sink_(7)
set ftp_(7) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(7) attach-agent $tcp_(7)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(7) start"
set tcp_(8) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(8) set class_ 2
set sink_(8) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(8) $tcp_(8)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(8) $sink_(8)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(8) $sink_(8)
set ftp_(8) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(8) attach-agent $tcp_(8)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(8) start"
set tcp_(9) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(9) set class_ 2
set sink_(9) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(9) $tcp_(9)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(9) $sink_(9)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(9) $sink_(9)
set ftp_(9) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(9) attach-agent $tcp_(9)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(9) start"
set tcp_(10) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(10) set class_ 2
set sink_(10) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(10) $tcp_(10)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(10) $sink_(10)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(10) $sink_(10)
set ftp_(10) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(10) attach-agent $tcp_(10)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(10) start"
set tcp_(11) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(11) set class_ 2
set sink_(11) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(11) $tcp_(11)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(11) $sink_(11)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(11) $sink_(11)
set ftp_(11) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(11) attach-agent $tcp_(11)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(11) start"
set tcp_(12) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(12) set class_ 2
set sink_(12) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(12) $tcp_(12)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(12) $sink_(12)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(12) $sink_(12)
set ftp_(12) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(12) attach-agent $tcp_(12)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(12) start"
set tcp_(13) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(13) set class_ 2
set sink_(13) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(13) $tcp_(13)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(13) $sink_(13)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(13) $sink_(13)
set ftp_(13) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(13) attach-agent $tcp_(13)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(13) start"
set tcp_(14) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(14) set class_ 2
set sink_(14) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(14) $tcp_(14)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(14) $sink_(14)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(14) $sink_(14)
set ftp_(14) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(14) attach-agent $tcp_(14)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(14) start"
set tcp_(15) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(15) set class_ 2
set sink_(15) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(15) $tcp_(15)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(15) $sink_(15)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(15) $sink_(15)
set ftp_(15) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(15) attach-agent $tcp_(15)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(15) start"
set tcp_(16) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(16) set class_ 2
set sink_(16) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(16) $tcp_(16)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(16) $sink_(16)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(16) $sink_(16)
set ftp_(16) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(16) attach-agent $tcp_(16)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(16) start"
set tcp_(17) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(17) set class_ 2
set sink_(17) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(17) $tcp_(17)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(17) $sink_(17)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(17) $sink_(17)
set ftp_(17) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(17) attach-agent $tcp_(17)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(17) start"
set tcp_(18) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(18) set class_ 2
set sink_(18) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(18) $tcp_(18)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(18) $sink_(18)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(18) $sink_(18)
set ftp_(18) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(18) attach-agent $tcp_(18)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(18) start"
set tcp_(19) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(19) set class_ 2
set sink_(19) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(19) $tcp_(19)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(19) $sink_(19)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(19) $sink_(19)
set ftp_(19) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(19) attach-agent $tcp_(19)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(19) start"
set tcp_(20) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(20) set class_ 2
set sink_(20) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(20) $tcp_(20)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(20) $sink_(20)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(20) $sink_(20)
set ftp_(20) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(20) attach-agent $tcp_(20)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(20) start"
set tcp_(21) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(21) set class_ 2
set sink_(21) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(21) $tcp_(21)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(21) $sink_(21)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(21) $sink_(21)
set ftp_(21) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(21) attach-agent $tcp_(21)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(21) start"
set tcp_(22) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(22) set class_ 2
set sink_(22) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(22) $tcp_(22)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(22) $sink_(22)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(22) $sink_(22)
set ftp_(22) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(22) attach-agent $tcp_(22)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(22) start"
set tcp_(23) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(23) set class_ 2
set sink_(23) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(23) $tcp_(23)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(23) $sink_(23)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(23) $sink_(23)
set ftp_(23) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(23) attach-agent $tcp_(23)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(23) start"
set tcp_(24) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(24) set class_ 2
set sink_(24) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(24) $tcp_(24)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(24) $sink_(24)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(24) $sink_(24)
set ftp_(24) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(24) attach-agent $tcp_(24)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(24) start"
set tcp_(25) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(25) set class_ 2
set sink_(25) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(25) $tcp_(25)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(25) $sink_(25)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(25) $sink_(25)
set ftp_(25) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(25) attach-agent $tcp_(25)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(25) start"
set tcp_(26) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(26) set class_ 2
set sink_(26) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(26) $tcp_(26)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(26) $sink_(26)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(26) $sink_(26)
set ftp_(26) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(26) attach-agent $tcp_(26)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(26) start"
set tcp_(27) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(27) set class_ 2
set sink_(27) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(27) $tcp_(27)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(27) $sink_(27)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(27) $sink_(27)
set ftp_(27) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(27) attach-agent $tcp_(27)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(27) start"
set tcp_(28) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(28) set class_ 2
set sink_(28) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(28) $tcp_(28)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(28) $sink_(28)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(28) $sink_(28)
set ftp_(28) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(28) attach-agent $tcp_(28)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(28) start"
set tcp_(29) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(29) set class_ 2
set sink_(29) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(29) $tcp_(29)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(29) $sink_(29)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(29) $sink_(29)
set ftp_(29) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(29) attach-agent $tcp_(29)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(29) start"
#up stream for TCP
set tcp_(60) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(60) set class_ 2
set sink_(60) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(0) $tcp_(60)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(0) $sink_(60)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(60) $sink_(60)
set ftp_(60) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(60) attach-agent $tcp_(60)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(60) start"
set tcp_(61) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(61) set class_ 2
set sink_(61) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(1) $tcp_(61)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(1) $sink_(61)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(61) $sink_(61)
set ftp_(61) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(61) attach-agent $tcp_(61)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(61) start"
set tcp_(62) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(62) set class_ 2
set sink_(62) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(2) $tcp_(62)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(2) $sink_(62)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(62) $sink_(62)
set ftp_(62) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(62) attach-agent $tcp_(62)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(62) start"
set tcp_(63) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(63) set class_ 2
set sink_(63) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(3) $tcp_(63)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(3) $sink_(63)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(63) $sink_(63)
set ftp_(63) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(63) attach-agent $tcp_(63)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(63) start"
set tcp_(64) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(64) set class_ 2
set sink_(64) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(4) $tcp_(64)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(4) $sink_(64)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(64) $sink_(64)
set ftp_(64) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(64) attach-agent $tcp_(64)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(64) start"
set tcp_(65) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(65) set class_ 2
set sink_(65) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(5) $tcp_(65)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(5) $sink_(65)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(65) $sink_(65)
set ftp_(65) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(65) attach-agent $tcp_(65)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(65) start"
set tcp_(66) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(66) set class_ 2
set sink_(66) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(6) $tcp_(66)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(6) $sink_(66)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(66) $sink_(66)
set ftp_(66) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(66) attach-agent $tcp_(66)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(66) start"
set tcp_(67) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(67) set class_ 2
set sink_(67) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(7) $tcp_(67)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(7) $sink_(67)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(67) $sink_(67)
set ftp_(67) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(67) attach-agent $tcp_(67)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(67) start"
set tcp_(68) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(68) set class_ 2
set sink_(68) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(8) $tcp_(68)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(8) $sink_(68)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(68) $sink_(68)
set ftp_(68) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(68) attach-agent $tcp_(68)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(68) start"
set tcp_(69) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(69) set class_ 2
set sink_(69) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(9) $tcp_(69)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(9) $sink_(69)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(69) $sink_(69)
set ftp_(69) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(69) attach-agent $tcp_(69)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(69) start"
set tcp_(70) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(70) set class_ 2
set sink_(70) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(10) $tcp_(70)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(10) $sink_(70)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(70) $sink_(70)
set ftp_(70) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(70) attach-agent $tcp_(70)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(70) start"
set tcp_(71) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(71) set class_ 2
set sink_(71) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(11) $tcp_(71)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(11) $sink_(71)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(71) $sink_(71)
set ftp_(71) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(71) attach-agent $tcp_(71)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(71) start"
set tcp_(72) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(72) set class_ 2
set sink_(72) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(12) $tcp_(72)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(12) $sink_(72)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(72) $sink_(72)
set ftp_(72) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(72) attach-agent $tcp_(72)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(72) start"
set tcp_(73) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(73) set class_ 2
set sink_(73) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(13) $tcp_(73)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(13) $sink_(73)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(73) $sink_(73)
set ftp_(73) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(73) attach-agent $tcp_(73)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(73) start"
set tcp_(74) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(74) set class_ 2
set sink_(74) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(14) $tcp_(74)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(14) $sink_(74)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(74) $sink_(74)
set ftp_(74) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(74) attach-agent $tcp_(74)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(74) start"
set tcp_(75) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(75) set class_ 2
set sink_(75) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(15) $tcp_(75)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(15) $sink_(75)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(75) $sink_(75)
set ftp_(75) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(75) attach-agent $tcp_(75)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(75) start"
set tcp_(76) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(76) set class_ 2
set sink_(76) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(16) $tcp_(76)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(16) $sink_(76)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(76) $sink_(76)
set ftp_(76) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(76) attach-agent $tcp_(76)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(76) start"
set tcp_(77) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(77) set class_ 2
set sink_(77) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(17) $tcp_(77)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(17) $sink_(77)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(77) $sink_(77)
set ftp_(77) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(77) attach-agent $tcp_(77)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(77) start"
set tcp_(78) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(78) set class_ 2
set sink_(78) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(18) $tcp_(78)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(18) $sink_(78)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(78) $sink_(78)
set ftp_(78) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(78) attach-agent $tcp_(78)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(78) start"
set tcp_(79) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(79) set class_ 2
set sink_(79) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(19) $tcp_(79)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(19) $sink_(79)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(79) $sink_(79)
set ftp_(79) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(79) attach-agent $tcp_(79)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(79) start"
set tcp_(80) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(80) set class_ 2
set sink_(80) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(20) $tcp_(80)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(20) $sink_(80)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(80) $sink_(80)
set ftp_(80) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(80) attach-agent $tcp_(80)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(80) start"
set tcp_(81) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(81) set class_ 2
set sink_(81) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(21) $tcp_(81)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(21) $sink_(81)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(81) $sink_(81)
set ftp_(81) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(81) attach-agent $tcp_(81)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(81) start"
set tcp_(82) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(82) set class_ 2
set sink_(82) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(22) $tcp_(82)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(22) $sink_(82)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(82) $sink_(82)
set ftp_(82) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(82) attach-agent $tcp_(82)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(82) start"
set tcp_(83) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(83) set class_ 2
set sink_(83) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(23) $tcp_(83)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(23) $sink_(83)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(83) $sink_(83)
set ftp_(83) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(83) attach-agent $tcp_(83)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(83) start"
set tcp_(84) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(84) set class_ 2
set sink_(84) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(24) $tcp_(84)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(24) $sink_(84)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(84) $sink_(84)
set ftp_(84) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(84) attach-agent $tcp_(84)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(84) start"
set tcp_(85) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(85) set class_ 2
set sink_(85) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(25) $tcp_(85)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(25) $sink_(85)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(85) $sink_(85)
set ftp_(85) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(85) attach-agent $tcp_(85)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(85) start"
set tcp_(86) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(86) set class_ 2
set sink_(86) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(26) $tcp_(86)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(26) $sink_(86)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(86) $sink_(86)
set ftp_(86) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(86) attach-agent $tcp_(86)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(86) start"
set tcp_(87) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(87) set class_ 2
set sink_(87) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(27) $tcp_(87)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(27) $sink_(87)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(87) $sink_(87)
set ftp_(87) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(87) attach-agent $tcp_(87)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(87) start"
set tcp_(88) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(88) set class_ 2
set sink_(88) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(28) $tcp_(88)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(28) $sink_(88)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(88) $sink_(88)
set ftp_(88) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(88) attach-agent $tcp_(88)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(88) start"
set tcp_(89) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(89) set class_ 2
set sink_(89) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(29) $tcp_(89)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(29) $sink_(89)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(89) $sink_(89)
set ftp_(89) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(89) attach-agent $tcp_(89)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(89) start"
#================================================
$ns_ at $opt(stop).0 "$BS(0) reset";
for {set t 0} {$t < $opt(mn)} {incr t} {
$ns_ at $opt(stop).0000010 "$node_($t) reset";
}
$ns_ at $opt(stop).1 "puts \"NS EXITING...\" ; $ns_ halt"
$ns_ at $opt(stop).0001 "stop"
proc stop {} {
global ns_ tracefd
# global ns_ namtracefd
close $tracefd
# close $namtracefd
}
# informative headers for CMUTracefile
#puts $tracefd "M 0.0 nn $opt(nm) x $opt(x) y $opt(y) rp \
# $opt(adhocRouting)"
#puts $tracefd "M 0.0 sc $opt(sc) cp $opt(cp) seed $opt(seed)"
#puts $tracefd "M 0.0 prop $opt(prop) ant $opt(ant)"
puts "Starting Simulation..."
$ns_ run
############################################################################
다음은 40개의 노드에 대한 tcl 파일이다.
파일명은 data40.tcl이다.
###########################################################################
### This simulation is an example of combination of wired and wireless
### topologies.
global opt
set opt(chan) Channel/WirelessChannel
set opt(prop) Propagation/TwoRayGround
set opt(netif) Phy/WirelessPhy
set opt(mac) Mac/802_11
set opt(ifq) Queue/DropTail/PriQueue
set opt(ll) LL
set opt(ant) Antenna/OmniAntenna
set opt(x) 500
set opt(y) 500
set opt(ifqlen) 50
set opt(adhocRouting) DSDV;#AODV ;#DSDV, DSR
set opt(cp) ""
set opt(sc) "../mobility/scene/scen-3-test"
set opt(stop) 500
set num_wired_nodes 2
set num_bs_nodes 1
set opt(mn) 40
set cmin [lindex $argv 0]
set cmax [lindex $argv 1]
set opt(nm) 41
Agent/TCP set packetSize_ 1480
# Mac/802_11 set RTSThreshold_ 99999
Mac/802_11 set dataRate_ 11.0e6 ;# 11Mbps
Mac/802_11 set basicRate_ 11.0e6 ;# 1Mbps
# ===========================================================
# 802.11b value
#The Antenna height of transmitter and receiver is 1.5m.
Phy/WirelessPhy set bandwidth_ 11Mb
#===============================================================
set ns_ [new Simulator]
# set up for hierarchical routing
$ns_ node-config -addressType hierarchical
AddrParams set domain_num_ 2 ;# number of domains
lappend cluster_num 1 1 ;# number of clusters in each domain
AddrParams set cluster_num_ $cluster_num
lappend eilastlevel $opt(nm) $opt(nm) ;# number of nodes in each cluster
AddrParams set nodes_num_ $eilastlevel ;# of each domain
set tracefd [open up_down_stream_$opt(mn)-$opt(mn)-$cmin-$cmax.tr w]
$ns_ trace-all $tracefd
# Create topography object
set topo [new Topography]
# define topology
$topo load_flatgrid $opt(x) $opt(y)
# create God
create-god $opt(nm)
set temp {0.0.0 0.0.1 0.0.2 0.0.3 0.0.4 0.0.5 0.0.6 0.0.7 0.0.8 0.0.9 0.0.10 0.0.11 0.0.12 0.0.13 0.0.14 0.0.15 0.0.16 0.0.17 0.0.18 0.0.19 0.0.20 0.0.21 0.0.22 0.0.23 0.0.24 0.0.25 0.0.26 0.0.27 0.0.28 0.0.29 0.0.30 0.0.31 0.0.32 0.0.33 0.0.34 0.0.35 0.0.36 0.0.37 0.0.38 0.0.39 0.0.40 0.0.41 0.0.42 0.0.43 0.0.44 0.0.45 0.0.46 0.0.47 0.0.48 0.0.49 0.0.50 0.0.51 0.0.52 0.0.53 0.0.54 0.0.55 0.0.56 0.0.57 0.0.58 0.0.59 0.0.60 0.0.61 0.0.62 0.0.63 0.0.64 0.0.65 0.0.66 0.0.67 0.0.68 0.0.69 0.0.70 0.0.71 0.0.72 0.0.73 0.0.74 0.0.75 0.0.76 0.0.77 0.0.78 0.0.79 0.0.80} ;# hierarchical addresses for wired domain
for {set i 0} {$i < $opt(nm)} {incr i} {
set W($i) [$ns_ node [lindex $temp $i]]
}
Mac/802_11 set CWMin_ $cmin
Mac/802_11 set CWMax_ $cmax
puts "CW value : $cmin $cmax"
#Mac/802_11 set ShortRetryLimit_ 7 ;# retransmittions
#Mac/802_11 set LongRetryLimit_ 4 ;# retransmissions
$ns_ node-config -adhocRouting $opt(adhocRouting) \
-llType $opt(ll) \
-macType $opt(mac) \
-ifqType $opt(ifq) \
-ifqLen $opt(ifqlen) \
-antType $opt(ant) \
-propType $opt(prop) \
-phyType $opt(netif) \
-channelType $opt(chan) \
-topoInstance $topo \
-wiredRouting ON \
-agentTrace ON \
-routerTrace OFF \
-macTrace OFF \
set temp {1.0.0 1.0.1 1.0.2 1.0.3 1.0.4 1.0.5 1.0.6 1.0.7 1.0.8 1.0.9 1.0.10 1.0.11 1.0.12 1.0.13 1.0.14 1.0.15 1.0.16 1.0.17 1.0.18 1.0.19 1.0.20 1.0.21 1.0.22 1.0.23 1.0.24 1.0.25 1.0.26 1.0.27 1.0.28 1.0.29 1.0.30 1.0.31 1.0.32 1.0.33 1.0.34 1.0.35 1.0.36 1.0.37 1.0.38 1.0.39 1.0.40 1.0.41 1.0.42 1.0.43 1.0.44 1.0.45 1.0.46 1.0.47 1.0.48 1.0.49 1.0.50 1.0.51 1.0.52 1.0.53 1.0.54 1.0.55 1.0.56 1.0.57 1.0.58 1.0.59 1.0.60 1.0.61 1.0.62 1.0.63 1.0.64 1.0.65 1.0.66 1.0.67 1.0.68 1.0.69 1.0.70 1.0.71 1.0.72 1.0.73 1.0.74 1.0.75 1.0.76 1.0.77 1.0.78 1.0.79 1.0.80} ;# hier address to be used for wireless
set BS(0) [$ns_ node [lindex $temp 0]]
$BS(0) random-motion 0
Mac/802_11 set CWMin_ 31
Mac/802_11 set CWMax_ 1023
# Mac/802_11 set ShortRetryLimit_ 7 ;# retransmittions
# Mac/802_11 set LongRetryLimit_ 4 ;# retransmissions
$ns_ node-config -adhocRouting $opt(adhocRouting) \
-llType $opt(ll) \
-macType $opt(mac) \
-ifqType $opt(ifq) \
-ifqLen $opt(ifqlen) \
-antType $opt(ant) \
-propType $opt(prop) \
-phyType $opt(netif) \
-channelType $opt(chan) \
-topoInstance $topo \
-wiredRouting ON \
-agentTrace ON \
-routerTrace OFF \
-macTrace OFF \
for {set j 0} {$j < $opt(mn)} {incr j} {
set node_($j) [ $ns_ node [lindex $temp \
[expr $j+1]] ]
$node_($j) base-station [AddrParams addr2id [$BS(0) node-addr]]
}
$ns_ duplex-link $W(0) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(1) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(2) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(3) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(4) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(5) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(6) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(7) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(8) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(9) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(10) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(11) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(12) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(13) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(14) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(15) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(16) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(17) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(18) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(19) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(20) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(21) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(22) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(23) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(24) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(25) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(26) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(27) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(28) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(29) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(30) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(31) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(32) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(33) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(34) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(35) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(36) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(37) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(38) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(39) $W(40) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
$ns_ duplex-link $W(40) $BS(0) 100Mb 100ms DropTail
#===============================================================
#down strem for TCP
set tcp_(0) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(0) set class_ 2
set sink_(0) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(0) $tcp_(0)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(0) $sink_(0)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(0) $sink_(0)
set ftp_(0) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(0) attach-agent $tcp_(0)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(0) start"
set tcp_(1) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(1) set class_ 2
set sink_(1) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(1) $tcp_(1)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(1) $sink_(1)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(1) $sink_(1)
set ftp_(1) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(1) attach-agent $tcp_(1)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(1) start"
set tcp_(2) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(2) set class_ 2
set sink_(2) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(2) $tcp_(2)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(2) $sink_(2)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(2) $sink_(2)
set ftp_(2) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(2) attach-agent $tcp_(2)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(2) start"
set tcp_(3) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(3) set class_ 2
set sink_(3) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(3) $tcp_(3)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(3) $sink_(3)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(3) $sink_(3)
set ftp_(3) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(3) attach-agent $tcp_(3)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(3) start"
set tcp_(4) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(4) set class_ 2
set sink_(4) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(4) $tcp_(4)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(4) $sink_(4)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(4) $sink_(4)
set ftp_(4) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(4) attach-agent $tcp_(4)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(4) start"
set tcp_(5) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(5) set class_ 2
set sink_(5) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(5) $tcp_(5)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(5) $sink_(5)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(5) $sink_(5)
set ftp_(5) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(5) attach-agent $tcp_(5)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(5) start"
set tcp_(6) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(6) set class_ 2
set sink_(6) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(6) $tcp_(6)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(6) $sink_(6)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(6) $sink_(6)
set ftp_(6) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(6) attach-agent $tcp_(6)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(6) start"
set tcp_(7) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(7) set class_ 2
set sink_(7) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(7) $tcp_(7)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(7) $sink_(7)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(7) $sink_(7)
set ftp_(7) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(7) attach-agent $tcp_(7)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(7) start"
set tcp_(8) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(8) set class_ 2
set sink_(8) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(8) $tcp_(8)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(8) $sink_(8)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(8) $sink_(8)
set ftp_(8) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(8) attach-agent $tcp_(8)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(8) start"
set tcp_(9) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(9) set class_ 2
set sink_(9) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(9) $tcp_(9)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(9) $sink_(9)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(9) $sink_(9)
set ftp_(9) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(9) attach-agent $tcp_(9)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(9) start"
set tcp_(10) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(10) set class_ 2
set sink_(10) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(10) $tcp_(10)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(10) $sink_(10)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(10) $sink_(10)
set ftp_(10) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(10) attach-agent $tcp_(10)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(10) start"
set tcp_(11) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(11) set class_ 2
set sink_(11) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(11) $tcp_(11)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(11) $sink_(11)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(11) $sink_(11)
set ftp_(11) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(11) attach-agent $tcp_(11)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(11) start"
set tcp_(12) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(12) set class_ 2
set sink_(12) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(12) $tcp_(12)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(12) $sink_(12)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(12) $sink_(12)
set ftp_(12) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(12) attach-agent $tcp_(12)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(12) start"
set tcp_(13) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(13) set class_ 2
set sink_(13) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(13) $tcp_(13)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(13) $sink_(13)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(13) $sink_(13)
set ftp_(13) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(13) attach-agent $tcp_(13)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(13) start"
set tcp_(14) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(14) set class_ 2
set sink_(14) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(14) $tcp_(14)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(14) $sink_(14)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(14) $sink_(14)
set ftp_(14) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(14) attach-agent $tcp_(14)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(14) start"
set tcp_(15) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(15) set class_ 2
set sink_(15) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(15) $tcp_(15)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(15) $sink_(15)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(15) $sink_(15)
set ftp_(15) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(15) attach-agent $tcp_(15)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(15) start"
set tcp_(16) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(16) set class_ 2
set sink_(16) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(16) $tcp_(16)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(16) $sink_(16)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(16) $sink_(16)
set ftp_(16) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(16) attach-agent $tcp_(16)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(16) start"
set tcp_(17) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(17) set class_ 2
set sink_(17) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(17) $tcp_(17)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(17) $sink_(17)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(17) $sink_(17)
set ftp_(17) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(17) attach-agent $tcp_(17)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(17) start"
set tcp_(18) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(18) set class_ 2
set sink_(18) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(18) $tcp_(18)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(18) $sink_(18)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(18) $sink_(18)
set ftp_(18) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(18) attach-agent $tcp_(18)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(18) start"
set tcp_(19) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(19) set class_ 2
set sink_(19) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(19) $tcp_(19)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(19) $sink_(19)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(19) $sink_(19)
set ftp_(19) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(19) attach-agent $tcp_(19)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(19) start"
set tcp_(20) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(20) set class_ 2
set sink_(20) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(20) $tcp_(20)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(20) $sink_(20)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(20) $sink_(20)
set ftp_(20) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(20) attach-agent $tcp_(20)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(20) start"
set tcp_(21) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(21) set class_ 2
set sink_(21) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(21) $tcp_(21)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(21) $sink_(21)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(21) $sink_(21)
set ftp_(21) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(21) attach-agent $tcp_(21)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(21) start"
set tcp_(22) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(22) set class_ 2
set sink_(22) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(22) $tcp_(22)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(22) $sink_(22)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(22) $sink_(22)
set ftp_(22) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(22) attach-agent $tcp_(22)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(22) start"
set tcp_(23) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(23) set class_ 2
set sink_(23) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(23) $tcp_(23)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(23) $sink_(23)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(23) $sink_(23)
set ftp_(23) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(23) attach-agent $tcp_(23)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(23) start"
set tcp_(24) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(24) set class_ 2
set sink_(24) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(24) $tcp_(24)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(24) $sink_(24)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(24) $sink_(24)
set ftp_(24) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(24) attach-agent $tcp_(24)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(24) start"
set tcp_(25) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(25) set class_ 2
set sink_(25) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(25) $tcp_(25)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(25) $sink_(25)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(25) $sink_(25)
set ftp_(25) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(25) attach-agent $tcp_(25)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(25) start"
set tcp_(26) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(26) set class_ 2
set sink_(26) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(26) $tcp_(26)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(26) $sink_(26)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(26) $sink_(26)
set ftp_(26) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(26) attach-agent $tcp_(26)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(26) start"
set tcp_(27) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(27) set class_ 2
set sink_(27) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(27) $tcp_(27)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(27) $sink_(27)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(27) $sink_(27)
set ftp_(27) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(27) attach-agent $tcp_(27)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(27) start"
set tcp_(28) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(28) set class_ 2
set sink_(28) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(28) $tcp_(28)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(28) $sink_(28)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(28) $sink_(28)
set ftp_(28) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(28) attach-agent $tcp_(28)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(28) start"
set tcp_(29) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(29) set class_ 2
set sink_(29) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(29) $tcp_(29)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(29) $sink_(29)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(29) $sink_(29)
set ftp_(29) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(29) attach-agent $tcp_(29)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(29) start"
set tcp_(30) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(30) set class_ 2
set sink_(30) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(30) $tcp_(30)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(30) $sink_(30)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(30) $sink_(30)
set ftp_(30) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(30) attach-agent $tcp_(30)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(30) start"
set tcp_(31) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(31) set class_ 2
set sink_(31) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(31) $tcp_(31)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(31) $sink_(31)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(31) $sink_(31)
set ftp_(31) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(31) attach-agent $tcp_(31)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(31) start"
set tcp_(32) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(32) set class_ 2
set sink_(32) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(32) $tcp_(32)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(32) $sink_(32)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(32) $sink_(32)
set ftp_(32) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(32) attach-agent $tcp_(32)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(32) start"
set tcp_(33) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(33) set class_ 2
set sink_(33) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(33) $tcp_(33)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(33) $sink_(33)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(33) $sink_(33)
set ftp_(33) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(33) attach-agent $tcp_(33)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(33) start"
set tcp_(34) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(34) set class_ 2
set sink_(34) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(34) $tcp_(34)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(34) $sink_(34)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(34) $sink_(34)
set ftp_(34) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(34) attach-agent $tcp_(34)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(34) start"
set tcp_(35) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(35) set class_ 2
set sink_(35) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(35) $tcp_(35)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(35) $sink_(35)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(35) $sink_(35)
set ftp_(35) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(35) attach-agent $tcp_(35)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(35) start"
set tcp_(36) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(36) set class_ 2
set sink_(36) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(36) $tcp_(36)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(36) $sink_(36)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(36) $sink_(36)
set ftp_(36) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(36) attach-agent $tcp_(36)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(36) start"
set tcp_(37) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(37) set class_ 2
set sink_(37) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(37) $tcp_(37)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(37) $sink_(37)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(37) $sink_(37)
set ftp_(37) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(37) attach-agent $tcp_(37)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(37) start"
set tcp_(38) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(38) set class_ 2
set sink_(38) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(38) $tcp_(38)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(38) $sink_(38)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(38) $sink_(38)
set ftp_(38) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(38) attach-agent $tcp_(38)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(38) start"
set tcp_(39) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(39) set class_ 2
set sink_(39) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $W(39) $tcp_(39)
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(39) $sink_(39)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(39) $sink_(39)
set ftp_(39) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(39) attach-agent $tcp_(39)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(39) start"
#up stream for TCP
set tcp_(60) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(60) set class_ 2
set sink_(60) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(0) $tcp_(60)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(0) $sink_(60)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(60) $sink_(60)
set ftp_(60) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(60) attach-agent $tcp_(60)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(60) start"
set tcp_(61) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(61) set class_ 2
set sink_(61) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(1) $tcp_(61)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(1) $sink_(61)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(61) $sink_(61)
set ftp_(61) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(61) attach-agent $tcp_(61)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(61) start"
set tcp_(62) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(62) set class_ 2
set sink_(62) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(2) $tcp_(62)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(2) $sink_(62)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(62) $sink_(62)
set ftp_(62) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(62) attach-agent $tcp_(62)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(62) start"
set tcp_(63) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(63) set class_ 2
set sink_(63) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(3) $tcp_(63)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(3) $sink_(63)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(63) $sink_(63)
set ftp_(63) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(63) attach-agent $tcp_(63)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(63) start"
set tcp_(64) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(64) set class_ 2
set sink_(64) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(4) $tcp_(64)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(4) $sink_(64)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(64) $sink_(64)
set ftp_(64) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(64) attach-agent $tcp_(64)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(64) start"
set tcp_(65) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(65) set class_ 2
set sink_(65) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(5) $tcp_(65)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(5) $sink_(65)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(65) $sink_(65)
set ftp_(65) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(65) attach-agent $tcp_(65)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(65) start"
set tcp_(66) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(66) set class_ 2
set sink_(66) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(6) $tcp_(66)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(6) $sink_(66)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(66) $sink_(66)
set ftp_(66) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(66) attach-agent $tcp_(66)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(66) start"
set tcp_(67) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(67) set class_ 2
set sink_(67) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(7) $tcp_(67)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(7) $sink_(67)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(67) $sink_(67)
set ftp_(67) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(67) attach-agent $tcp_(67)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(67) start"
set tcp_(68) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(68) set class_ 2
set sink_(68) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(8) $tcp_(68)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(8) $sink_(68)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(68) $sink_(68)
set ftp_(68) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(68) attach-agent $tcp_(68)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(68) start"
set tcp_(69) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(69) set class_ 2
set sink_(69) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(9) $tcp_(69)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(9) $sink_(69)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(69) $sink_(69)
set ftp_(69) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(69) attach-agent $tcp_(69)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(69) start"
set tcp_(70) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(70) set class_ 2
set sink_(70) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(10) $tcp_(70)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(10) $sink_(70)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(70) $sink_(70)
set ftp_(70) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(70) attach-agent $tcp_(70)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(70) start"
set tcp_(71) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(71) set class_ 2
set sink_(71) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(11) $tcp_(71)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(11) $sink_(71)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(71) $sink_(71)
set ftp_(71) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(71) attach-agent $tcp_(71)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(71) start"
set tcp_(72) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(72) set class_ 2
set sink_(72) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(12) $tcp_(72)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(12) $sink_(72)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(72) $sink_(72)
set ftp_(72) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(72) attach-agent $tcp_(72)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(72) start"
set tcp_(73) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(73) set class_ 2
set sink_(73) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(13) $tcp_(73)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(13) $sink_(73)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(73) $sink_(73)
set ftp_(73) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(73) attach-agent $tcp_(73)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(73) start"
set tcp_(74) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(74) set class_ 2
set sink_(74) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(14) $tcp_(74)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(14) $sink_(74)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(74) $sink_(74)
set ftp_(74) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(74) attach-agent $tcp_(74)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(74) start"
set tcp_(75) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(75) set class_ 2
set sink_(75) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(15) $tcp_(75)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(15) $sink_(75)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(75) $sink_(75)
set ftp_(75) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(75) attach-agent $tcp_(75)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(75) start"
set tcp_(76) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(76) set class_ 2
set sink_(76) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(16) $tcp_(76)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(16) $sink_(76)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(76) $sink_(76)
set ftp_(76) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(76) attach-agent $tcp_(76)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(76) start"
set tcp_(77) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(77) set class_ 2
set sink_(77) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(17) $tcp_(77)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(17) $sink_(77)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(77) $sink_(77)
set ftp_(77) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(77) attach-agent $tcp_(77)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(77) start"
set tcp_(78) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(78) set class_ 2
set sink_(78) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(18) $tcp_(78)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(18) $sink_(78)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(78) $sink_(78)
set ftp_(78) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(78) attach-agent $tcp_(78)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(78) start"
set tcp_(79) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(79) set class_ 2
set sink_(79) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(19) $tcp_(79)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(19) $sink_(79)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(79) $sink_(79)
set ftp_(79) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(79) attach-agent $tcp_(79)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(79) start"
set tcp_(80) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(80) set class_ 2
set sink_(80) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(20) $tcp_(80)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(20) $sink_(80)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(80) $sink_(80)
set ftp_(80) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(80) attach-agent $tcp_(80)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(80) start"
set tcp_(81) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(81) set class_ 2
set sink_(81) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(21) $tcp_(81)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(21) $sink_(81)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(81) $sink_(81)
set ftp_(81) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(81) attach-agent $tcp_(81)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(81) start"
set tcp_(82) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(82) set class_ 2
set sink_(82) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(22) $tcp_(82)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(22) $sink_(82)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(82) $sink_(82)
set ftp_(82) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(82) attach-agent $tcp_(82)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(82) start"
set tcp_(83) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(83) set class_ 2
set sink_(83) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(23) $tcp_(83)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(23) $sink_(83)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(83) $sink_(83)
set ftp_(83) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(83) attach-agent $tcp_(83)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(83) start"
set tcp_(84) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(84) set class_ 2
set sink_(84) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(24) $tcp_(84)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(24) $sink_(84)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(84) $sink_(84)
set ftp_(84) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(84) attach-agent $tcp_(84)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(84) start"
set tcp_(85) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(85) set class_ 2
set sink_(85) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(25) $tcp_(85)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(25) $sink_(85)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(85) $sink_(85)
set ftp_(85) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(85) attach-agent $tcp_(85)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(85) start"
set tcp_(86) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(86) set class_ 2
set sink_(86) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(26) $tcp_(86)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(26) $sink_(86)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(86) $sink_(86)
set ftp_(86) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(86) attach-agent $tcp_(86)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(86) start"
set tcp_(87) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(87) set class_ 2
set sink_(87) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(27) $tcp_(87)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(27) $sink_(87)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(87) $sink_(87)
set ftp_(87) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(87) attach-agent $tcp_(87)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(87) start"
set tcp_(88) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(88) set class_ 2
set sink_(88) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(28) $tcp_(88)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(28) $sink_(88)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(88) $sink_(88)
set ftp_(88) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(88) attach-agent $tcp_(88)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(88) start"
set tcp_(89) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(89) set class_ 2
set sink_(89) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(29) $tcp_(89)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(29) $sink_(89)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(89) $sink_(89)
set ftp_(89) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(89) attach-agent $tcp_(89)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(89) start"
set tcp_(90) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(90) set class_ 2
set sink_(90) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(30) $tcp_(90)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(30) $sink_(90)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(90) $sink_(90)
set ftp_(90) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(90) attach-agent $tcp_(90)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(90) start"
set tcp_(91) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(91) set class_ 2
set sink_(91) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(31) $tcp_(91)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(31) $sink_(91)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(91) $sink_(91)
set ftp_(91) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(91) attach-agent $tcp_(91)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(91) start"
set tcp_(92) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(92) set class_ 2
set sink_(92) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(32) $tcp_(92)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(32) $sink_(92)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(92) $sink_(92)
set ftp_(92) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(92) attach-agent $tcp_(92)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(92) start"
set tcp_(93) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(93) set class_ 2
set sink_(93) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(33) $tcp_(93)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(33) $sink_(93)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(93) $sink_(93)
set ftp_(93) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(93) attach-agent $tcp_(93)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(93) start"
set tcp_(94) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(94) set class_ 2
set sink_(94) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(34) $tcp_(94)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(34) $sink_(94)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(94) $sink_(94)
set ftp_(94) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(94) attach-agent $tcp_(94)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(94) start"
set tcp_(95) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(95) set class_ 2
set sink_(95) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(35) $tcp_(95)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(35) $sink_(95)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(95) $sink_(95)
set ftp_(95) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(95) attach-agent $tcp_(95)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(95) start"
set tcp_(96) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(96) set class_ 2
set sink_(96) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(36) $tcp_(96)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(36) $sink_(96)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(96) $sink_(96)
set ftp_(96) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(96) attach-agent $tcp_(96)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(96) start"
set tcp_(97) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(97) set class_ 2
set sink_(97) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(37) $tcp_(97)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(37) $sink_(97)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(97) $sink_(97)
set ftp_(97) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(97) attach-agent $tcp_(97)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(97) start"
set tcp_(98) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(98) set class_ 2
set sink_(98) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(38) $tcp_(98)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(38) $sink_(98)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(98) $sink_(98)
set ftp_(98) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(98) attach-agent $tcp_(98)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(98) start"
set tcp_(99) [new Agent/TCP/Reno]
$tcp_(99) set class_ 2
set sink_(99) [new Agent/TCPSink]
$ns_ attach-agent $node_(39) $tcp_(99)
$ns_ attach-agent $W(39) $sink_(99)
$ns_ connect $tcp_(99) $sink_(99)
set ftp_(99) [new Application/FTP]
$ftp_(99) attach-agent $tcp_(99)
$ns_ at 100 "$ftp_(99) start"
#================================================
$ns_ at $opt(stop).0 "$BS(0) reset";
for {set t 0} {$t < $opt(mn)} {incr t} {
$ns_ at $opt(stop).0000010 "$node_($t) reset";
}
$ns_ at $opt(stop).1 "puts \"NS EXITING...\" ; $ns_ halt"
$ns_ at $opt(stop).0001 "stop"
proc stop {} {
global ns_ tracefd
# global ns_ namtracefd
close $tracefd
# close $namtracefd
}
# informative headers for CMUTracefile
#puts $tracefd "M 0.0 nn $opt(nm) x $opt(x) y $opt(y) rp \
# $opt(adhocRouting)"
#puts $tracefd "M 0.0 sc $opt(sc) cp $opt(cp) seed $opt(seed)"
#puts $tracefd "M 0.0 prop $opt(prop) ant $opt(ant)"
puts "Starting Simulation..."
$ns_ run
'Network > Simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 필요하면 어디서든 선언해 놓아야 한다... ns2 WLAN (0) | 2009.02.03 |
|---|---|
| DIFS제어 방법 ns2 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| NS2에서 802_11의 재전송 수 포기에 따른 카운터를 세고 싶을 때 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| ns2 코드에서 재전송 수를 직접 제어할 때! (0) | 2009.02.03 |
| 지금까지 실험한 결과들의 엑셀 파일 (0) | 2009.02.03 |
다운
'Network > How_to_study' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유무선통합(FMC)의 의미와 전망 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
|---|---|
| SMSC(Short Message Service Center) (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| 이동통신 기술 발전사 2 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| 무선 LAN 전송방식 비교 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| Wi-Fi, Wibro, WIPI, Bluetooth 정의 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
이것은 무선 단말기에서의 재전송 수가 7번을 넘어 패킷을 포기하게 되는 경우가 증가하게 되기 때문이었으며 30개의 단말에서의 공평성을 제공하기 위한 재전송 수 제어에 따른 실험 결과는 다음과 같다.
'Network > Ns2_simulation' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ns2 802.11 MAC에서 현제 큐의 size를 알 수 있는 방법. (0) | 2009.02.18 |
|---|---|
| TCP와 UDP (0) | 2009.02.18 |
| 거지같은... 논문들... ㅡㅡㅋ 믿을게 없다. ns2 802.11b udp 실험에서.. (1) | 2009.02.09 |
인터넷 이전에 지난 한 세기를 지배한 통신의 기본은 전화였습니다. 사람들은 웹브라우저에서 세상을 보고, 이메일과 메신저로 24시간 잠들지 않는 세상을 경험하고 있지만, 전화 또한 여전히 중요한 통신수단중 하나 입니다.
전화망(PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network)은 오랜세월동안 전세계에 충분히 구축 되었고, 다양한 시행착오를 거쳐 현재 안정적으로 운영되고 있습니다. 전화는 일반 대중에게는 가장 친숙하고 매우 신뢰성이 높은 통신매체라고 할 수 있습니다.
인터넷의 경우는 어떨까요? 전세계적으로 대중에 알려지기 시작하며 급속도로 망이 구축된것이 90년대 후반이므로 아직 20년도 안된 역사를 가지고 있습니다. 초창기에 비하면 지금은 인터넷망의 안정성도 매우 높아졌지만, 태생자체가 인터넷은 안정성보다 생존성에 그리고 폐쇄성보다는 개방성에 촛점이 맞춰 있기 때문에 기존 전화망과 직접접인 비교는 어려울 것 같습니다.
인터넷전화(VoIP:Voice over IP)는 기존 전화망의 신뢰성보다는 인터넷망의 개방성에 더 촛점을 맞춘 전화서비스라고 볼 수 있습니다. 예전에는 통화품질 면에서는 전화망이 월등히 좋았으나, 기술의 발전은 이 격차마저 줄여가고 있습니다.
인터넷전화는 폐쇄된 PSTN 대신 공개된 인터넷망을 이용할 뿐입니다. 전화가입자는 인터넷만 되는곳이면 어디서나 전화를 이용할 수 있어 사실상 지역구분(시내,시외,국제)도 사라지는 개념이고 사업자는 고가의 장비가 없어도 전화서비스가 가능해 요금도 저렴한 장점이 있습니다.
결국 90년대 후반 국내에도 무료 인터넷전화(VoIP) '다이얼패드'가 최초로 등장해 많은 파란을 일으켰습니다. PC에서 헤드셋을 갖추고 통화를 해야하므로, 일반전화보다는 불편하고 통화품질도 다소 열악했지만, 사실상 무료통화를 제공함으로서 사람들의 관심을 집중시킬 수 있었습니다.
다만 서비스사 내부사정으로 서비스가 오래가진 못했지만, 이 일을 계기로 이용자와 통신사업자 모두는 기존 전화망 위주의 통신서비스 구도가, 인터넷망 중심으로 재편될 것이라는 것을 인지할 수 있었습니다.
하지만 수년의 시간이 흘렀지만 지금도 크게 달라진것은 없어보입니다. 그 사이 관련 기술의 발전은 계속되 왔지만 제도적으론 기존 전화사업자의 수익 악화에 따른 대응책 마련이 쉽지 않기 때문입니다.
이놈?~ 이넘(ENUM)!!
이와같이 90년대 후반 우리나라뿐 아니라 세계적으로도 전화가 인터넷의 영역으로 넘어오기 시작하면서, 사람들은 인터넷주소와 전화번호와의 연결 가능성에 대해 생각해 보기 시작했습니다.
그러던중 2001년경, 인터넷기술표준을 제정하는 IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force)에 ENUM WG(Working Group)생기고, 전화번호 표준을 담당하는 ITU와도 협력해 본격적으로 ENUM 기술표준을 제정하기 시작합니다.
개념은 간단합니다. 누군가의 전화번호 하나만 알면 다양한 응용프로그램을 통해 그 사람의 홈페이지에 접속하고, 인터넷전화도 걸고, 이메일 및 팩스도 보낼수 있게 하자는 것입니다. 예를 들어 ENUM번호가 있다면 명함을 만들때, 사무실 전화번호, 개인 핸드폰 번호, 메일주소, 홈페이지주소 등 온갖 정보를 다 넣지 않아도 ENUM번호 하나만 적어주면 됩니다. 명함을 받은 사람은 PC나 ENUM이 지원되는 휴대용기기 등에서 ENUM번호를 이용해 필요한 서비스를 선택할 수 있습니다.

단순히 생각하면 통신사업자가 개별적으로 제공하는 원넘버 서비스와 다를게 없이 보이지만, ENUM은 인터넷 기반기술인 DNS(Domain Name System)를 이용하고, 전세계 전화번호 표준인 ITU의 'E.164 권고안'을 따름으로서 최종적으론 전화망과 인터넷망의 융합(Convergence)을 가능케하는 전세계 공통표준 이라는 점에서 다릅니다. 즉, ENUM의 본질은 전화망과 인터넷망 사이에서 의사소통을 위한 "동시통역사"의 역할이라고 볼 수 있습니다. (예: 전화번호를 --> 인터넷식별자로 바꿔줌)
ENUM과 DNS(Domain Name System)
기술적으로 ENUM을 이해하기 위해서는 먼저 DNS를 이해해야 합니다. DNS서버는 도메인네임(예:www.naver.com)을 그에 대응하는 IP주소로(예:222.122.84.250) 변환시켜 주는 역할을 하는 인터넷 사용에 있어 매우 중요한 서버로, 이와 같은 정보는 어느 한 서버에 있는것이 아니라, 아래 그림과 같이 '루트(근원)' 부터 시작하여 국가별, 회사별로 체계에 따라 여러 관련 서버에 분산되어 있습니다. 따라서 특정 정보를 찾기 위해서는 상위의 루트부터 시작하여 점점 하위단계로 내려가면서 여러번의 검색을 수행해야 최종정보에 접근할 수 있습니다.
<그림 출처: 한국인터넷진흥원, 도메인네임시스템은 계층적인 tree구조를 가진다.>
*DNS관련 참고자료
- Powered by DNS : http://www.kr.freebsd.org/doc/PoweredByDNS/
- 위키피디아 자료(영문) : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_name_system
- 한국인터넷진흥원 : http://domain.nic.or.kr/infomation/class.jsp
ENUM에서는 DNS서버에 도메인과 IP주소 대신 전화번호와 그에 대응하는 홈페이지주소, 메일주소, 팩스번호등을 인터넷식별자(URI: Uniform Resource Identifier) 형태로 저장하여 사용합니다.
그리고, 전세계 통용이 가능하게 하기위해, ENUM전용 도메인을 생성하여 사용하고 있습니다. 아래 그림과 같이 "e164.arpa" 라는 도메인을 루트도메인 아래 생성하여, 전세계의 모든 전화번호를 이 도메인 아래서 표현이 가능하게 했습니다.

ENUM의 또 다른 활용
지금까지 설명한 ENUM은 '이용자 ENUM'이라고 하여 초기 시작부터 최근까지의 개념이었고, 최근에는 '사업자 ENUM'이라는 개념으로 발전해 제2의 도약기를 맞이하고 있습니다.
사실, ENUM의 기본 개념이었던 '이용자 ENUM'은 표준이 제정되고 상당한 시일이 경과했으나, 개인 프라이버시 문제 등으로 전세계적으로 답보상태에 있습니다. 2006년 10월 현재 전세계적으로 다음의 6개 국가만이 '이용자 ENUM' 상용서비스를 운영하고 있으며, 대부분 등록건수는 미미한것으로 알려져 있습니다.
오스트리아(+43)
폴란드(+48)
루마니아(+40)
독일(+49)
네델란드(+31)
핀란드(+358)
'사업자ENUM(Infrastructure ENUM)'은 인터넷전화 사업자가 인터넷전화 호 소통을 목적으로 ENUM을 활용하는 방안입니다. 아래의 개념도는 한국인터넷진흥원의 http://www.enum.or.kr 사이트에서 발췌한 것으로 ENUM이 지금까지 설명한 내용과는 전혀 다른목적으로 사용되고 있다는 것을 알수 있습니다.

인터넷 이전에 지난 한 세기를 지배한 통신의 기본은 전화였습니다. 사람들은 웹브라우저에서 세상을 보고, 이메일과 메신저로 24시간 잠들지 않는 세상을 경험하고 있지만, 전화 또한 여전히 중요한 통신수단중 하나 입니다.
전화망(PSTN: Public Switched Telephone Network)은 오랜세월동안 전세계에 충분히 구축 되었고, 다양한 시행착오를 거쳐 현재 안정적으로 운영되고 있습니다. 전화는 일반 대중에게는 가장 친숙하고 매우 신뢰성이 높은 통신매체라고 할 수 있습니다.
인터넷의 경우는 어떨까요? 전세계적으로 대중에 알려지기 시작하며 급속도로 망이 구축된것이 90년대 후반이므로 아직 20년도 안된 역사를 가지고 있습니다. 초창기에 비하면 지금은 인터넷망의 안정성도 매우 높아졌지만, 태생자체가 인터넷은 안정성보다 생존성에 그리고 폐쇄성보다는 개방성에 촛점이 맞춰 있기 때문에 기존 전화망과 직접접인 비교는 어려울 것 같습니다.
인터넷전화(VoIP:Voice over IP)는 기존 전화망의 신뢰성보다는 인터넷망의 개방성에 더 촛점을 맞춘 전화서비스라고 볼 수 있습니다. 예전에는 통화품질 면에서는 전화망이 월등히 좋았으나, 기술의 발전은 이 격차마저 줄여가고 있습니다.
인터넷전화는 폐쇄된 PSTN 대신 공개된 인터넷망을 이용할 뿐입니다. 전화가입자는 인터넷만 되는곳이면 어디서나 전화를 이용할 수 있어 사실상 지역구분(시내,시외,국제)도 사라지는 개념이고 사업자는 고가의 장비가 없어도 전화서비스가 가능해 요금도 저렴한 장점이 있습니다.
결국 90년대 후반 국내에도 무료 인터넷전화(VoIP) '다이얼패드'가 최초로 등장해 많은 파란을 일으켰습니다. PC에서 헤드셋을 갖추고 통화를 해야하므로, 일반전화보다는 불편하고 통화품질도 다소 열악했지만, 사실상 무료통화를 제공함으로서 사람들의 관심을 집중시킬 수 있었습니다.
다만 서비스사 내부사정으로 서비스가 오래가진 못했지만, 이 일을 계기로 이용자와 통신사업자 모두는 기존 전화망 위주의 통신서비스 구도가, 인터넷망 중심으로 재편될 것이라는 것을 인지할 수 있었습니다.
하지만 수년의 시간이 흘렀지만 지금도 크게 달라진것은 없어보입니다. 그 사이 관련 기술의 발전은 계속되 왔지만 제도적으론 기존 전화사업자의 수익 악화에 따른 대응책 마련이 쉽지 않기 때문입니다.
이놈?~ 이넘(ENUM)!!
이와같이 90년대 후반 우리나라뿐 아니라 세계적으로도 전화가 인터넷의 영역으로 넘어오기 시작하면서, 사람들은 인터넷주소와 전화번호와의 연결 가능성에 대해 생각해 보기 시작했습니다.
그러던중 2001년경, 인터넷기술표준을 제정하는 IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force)에 ENUM WG(Working Group)생기고, 전화번호 표준을 담당하는 ITU와도 협력해 본격적으로 ENUM 기술표준을 제정하기 시작합니다.
개념은 간단합니다. 누군가의 전화번호 하나만 알면 다양한 응용프로그램을 통해 그 사람의 홈페이지에 접속하고, 인터넷전화도 걸고, 이메일 및 팩스도 보낼수 있게 하자는 것입니다. 예를 들어 ENUM번호가 있다면 명함을 만들때, 사무실 전화번호, 개인 핸드폰 번호, 메일주소, 홈페이지주소 등 온갖 정보를 다 넣지 않아도 ENUM번호 하나만 적어주면 됩니다. 명함을 받은 사람은 PC나 ENUM이 지원되는 휴대용기기 등에서 ENUM번호를 이용해 필요한 서비스를 선택할 수 있습니다.
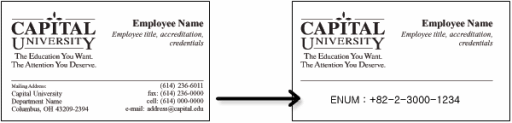
<명함예: 여러 연락처를 ENUM번호 하나로 표현>

단순히 생각하면 통신사업자가 개별적으로 제공하는 원넘버 서비스와 다를게 없이 보이지만, ENUM은 인터넷 기반기술인 DNS(Domain Name System)를 이용하고, 전세계 전화번호 표준인 ITU의 'E.164 권고안'을 따름으로서 최종적으론 전화망과 인터넷망의 융합(Convergence)을 가능케하는 전세계 공통표준 이라는 점에서 다릅니다. 즉, ENUM의 본질은 전화망과 인터넷망 사이에서 의사소통을 위한 "동시통역사"의 역할이라고 볼 수 있습니다. (예: 전화번호를 --> 인터넷식별자로 바꿔줌)
ENUM과 DNS(Domain Name System)
기술적으로 ENUM을 이해하기 위해서는 먼저 DNS를 이해해야 합니다. DNS서버는 도메인네임(예:www.naver.com)을 그에 대응하는 IP주소로(예:222.122.84.250) 변환시켜 주는 역할을 하는 인터넷 사용에 있어 매우 중요한 서버로, 이와 같은 정보는 어느 한 서버에 있는것이 아니라, 아래 그림과 같이 '루트(근원)' 부터 시작하여 국가별, 회사별로 체계에 따라 여러 관련 서버에 분산되어 있습니다. 따라서 특정 정보를 찾기 위해서는 상위의 루트부터 시작하여 점점 하위단계로 내려가면서 여러번의 검색을 수행해야 최종정보에 접근할 수 있습니다.
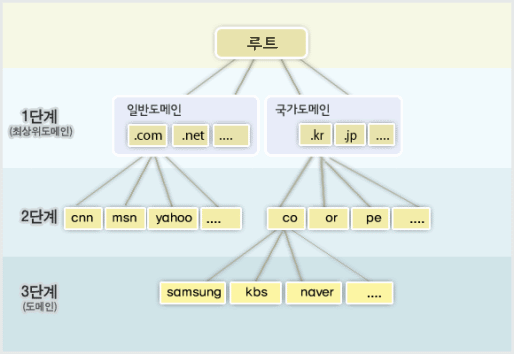
<그림 출처: 한국인터넷진흥원, 도메인네임시스템은 계층적인 tree구조를 가진다.>
*DNS관련 참고자료
- Powered by DNS : http://www.kr.freebsd.org/doc/PoweredByDNS/
- 위키피디아 자료(영문) : http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_name_system
- 한국인터넷진흥원 : http://domain.nic.or.kr/infomation/class.jsp
ENUM에서는 DNS서버에 도메인과 IP주소 대신 전화번호와 그에 대응하는 홈페이지주소, 메일주소, 팩스번호등을 인터넷식별자(URI: Uniform Resource Identifier) 형태로 저장하여 사용합니다.
그리고, 전세계 통용이 가능하게 하기위해, ENUM전용 도메인을 생성하여 사용하고 있습니다. 아래 그림과 같이 "e164.arpa" 라는 도메인을 루트도메인 아래 생성하여, 전세계의 모든 전화번호를 이 도메인 아래서 표현이 가능하게 했습니다.
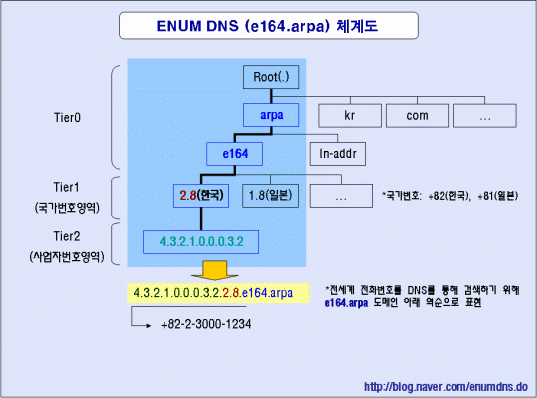
ENUM의 또 다른 활용
지금까지 설명한 ENUM은 '이용자 ENUM'이라고 하여 초기 시작부터 최근까지의 개념이었고, 최근에는 '사업자 ENUM'이라는 개념으로 발전해 제2의 도약기를 맞이하고 있습니다.
사실, ENUM의 기본 개념이었던 '이용자 ENUM'은 표준이 제정되고 상당한 시일이 경과했으나, 개인 프라이버시 문제 등으로 전세계적으로 답보상태에 있습니다. 2006년 10월 현재 전세계적으로 다음의 6개 국가만이 '이용자 ENUM' 상용서비스를 운영하고 있으며, 대부분 등록건수는 미미한것으로 알려져 있습니다.
오스트리아(+43)
폴란드(+48)
루마니아(+40)
독일(+49)
네델란드(+31)
핀란드(+358)
'사업자ENUM(Infrastructure ENUM)'은 인터넷전화 사업자가 인터넷전화 호 소통을 목적으로 ENUM을 활용하는 방안입니다. 아래의 개념도는 한국인터넷진흥원의 http://www.enum.or.kr 사이트에서 발췌한 것으로 ENUM이 지금까지 설명한 내용과는 전혀 다른목적으로 사용되고 있다는 것을 알수 있습니다.
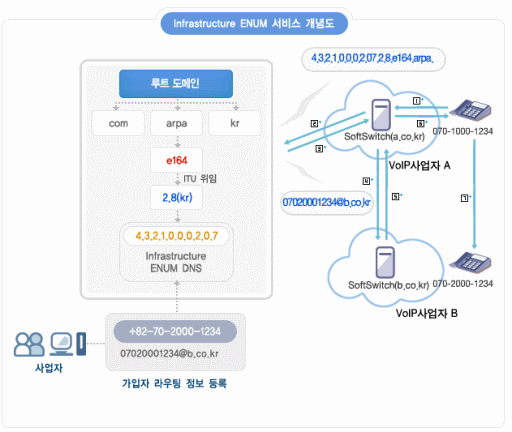
[출처] [본문스크랩] ENUM|작성자 문수
'Network > Netowrk_network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 실시간 통신 시스템 위한 VoIP 표준 프로토콜 H.323과 .. (0) | 2009.01.18 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Header (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| VoIP 관련 표준 문서 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| IP헤더 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| IP Header 와 IP 서비스의 특징 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
새로운 부가서비스 제공 유리 SIP’ … 상호 운용 솔루션 출시 눈앞
 이종석
이종석케이티인포텍 신사업기획단 상무
jslee@kti.co.k
지난 호에서는 이전의 음성통신망인 PSTN에 대해 살펴봤다. PSTN은 음성통신 서비스에 특화된 네트워크기 때문에 프로토콜 구조가 간단하며, 효율적으로 구성돼 있다. 그러나 인터넷을 위시한 패킷 네트워크는 파일전송 및 기타 실시간 통신을 목적으로 한 네트워크가 아니기 때문에 VoIP 등의 실시간 통신 시스템에는 여러 가지 특별한 프로토콜 및 기술들이 필요하다. 이번 호에서는 VoIP 시스템의 주요 프로토콜인 H.323과 SIP를 중심으로 VoIP 기술을 상세히 알아본다. <편집자>
현재 VoIP 시스템에서 가장 표준화된 프로토콜은 IETF(Internet Engineering Task Force)에서 발표한 SIP(Session Initiation Protocol)와 ITU-T(International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunication standardization sector)에서 제정한 H.323이다. 대부분의 VoIP 장비 판매업체 및 시스템 관련 산업은 두 가지 프로토콜을 모두 지원한다.
그러나 지난 2005년 7월 IETF에서 SIP와 H.323 프로토콜의 상호연동에 필요한 기술문서인 RFC(Request For Comments) 4123 SIP-H.323 Req.를 제정함에 따라, RFC 4123 초안에 근거해 상호연동이 가능한 제품이 근 시일내에 등장할 전망이다.
1. H.323
1) 개요
H.323은 인터넷을 포함한 패킷 네트워크에서 실시간 음성, 영상 및 데이터 통신을 위한 프로토콜이다. 최초 버전은 지난 1996년 ITU-T에 의해 승인됐으며, 현재 최종 발표된 H.323 버전은 5다. 가장 먼저 발표된 VoIP 지원 프로토콜로서 현재 가장 많이 사용되고 있는 H.323은 기존 네트워크의 하부구조를 변경하지 않고 멀티미디어 서비스를 사용할 수 있을 뿐 아니라 랜과 GSTN, N-ISDN, B-ISDN 등 다른 망과의 상호운용성에 대한 표준을 제공한다.
2) 구성 요소
H.323 시스템의 구성요소로는 단말(Terminal), 게이트웨이(Gateway), 게이트키퍼(Gatekeeper), MCU(Multipoint Control Unit)가 있다.
단말은 H.323 네트워크 내에서 이뤄지는 통신의 종단점이다. PC 및 H.323 단말기 등과 더불어 게이트웨이 MCU도 단말에 속한다. 게이트웨이는 H.323 프로토콜을 운용하는 네트워크와 H.323을 운용하지 않은 네트워크의 상호 정보교환 및 연동을 담당한다. 따라서 동일한 H.323 네트워크 내에서 H.323 단말들끼리의 통신에는 게이트웨이가 필요하지 않다.
게이트 키퍼는 단말, 게이트웨이, MCU 중 등록된 종단점에 대한 콜 컨트롤(call control)과 관련된 서비스를 제공하는 일종의 교환기다. H.323 네트워크 내에서는 선택적 구성요소로서 게이트키퍼가 있을 경우 모든 단말은 콜 제어와 관련해 게이트키퍼를 사용해야 하지만, 없을 경우에는 단말끼리의 통신으로 대체된다.
MCU는 3개 이상의 단말에 대한 다수통신을 가능하게 하는 기능을 수행한다. 다수 통신에 참여하는 모든 단말은 MCU와 연결을 설정해야 한다.
3) 프로토콜 구조
H.323을 구성하는 프로토콜로는 오디오 코덱, 비디오 코덱, H.225 RAS(Registration, Admission, Status) 프로토콜, H.225 콜 시그널링 프로토콜, H.245 콜 제어 프로토콜, RTP(Real-Time Transport Protocol), RTCP(Real-Time Transport Control Protocol) 등으로 구성된다.
4) 통신 과정
H.323을 이용한 1:1 통신은 크게 3가지의 방식으로 나뉜다. 첫 번째는 다이렉트 라우티드콜 시그널링(Direct Routed Call Signaling) 방식이다. 이 방식은 Q.931 및 H.245 메시지들을 게이트키퍼를 경유하지 않고 통신 당사자들만 직접 주고받는다. 두 번째는 게이트키퍼 라우티드 콜 시그널링(Gatekeeper Routed Call Signaling) 방식으로 Q.931, H.245 메시지들이 게이트키퍼를 경유해 주고받는다.
마지막으로는 게이트키퍼 라우티드 콜 시그널링 위드 다이렉트 H.245(Gatekeeper Routed Call Signaling with Direct H.245)는 게이트 키퍼는 콜 시그널링에 관여하고 H.245 메시지들만 통신 당사자들끼리 직접 주고받는 방식으로 가장 널리 사용된다.
1. 단말 1이 등록을 위해 RAS ARQ(Admission ReQuest)를 RAS 채널을 통해 게이트키퍼에 전송한다.
2. 게이트키퍼는 ACF(Admission ConFirmed)를 전송해 단말 1을 등록하며, 단말 1에 다이렉트 콜 시그널링이 가능하다는 것을 인증한다.
3. 단말 1은 H.225 콜 시그널링 셋업(call signaling Setup) 메시지를 단말 2에 보내 연결을 요청한다.
4. 단말 2는 H.225 콜 프로시딩(proceeding) 메시지로 응답한다.
5. 단말 2는 게이트키퍼에 RAS ARQ 메시지를 보내 게이트키퍼에 등록을 요청한다.
6. 게이트키퍼는 RAS ACF 메시지를 통해 등록 허가를 단말 2에 알린다.
7. 단말 2는 단말 1에게 H.225 콜 얼러팅(alerting) 메시지를 전송한다.
8. 마지막으로 단말 2는 H.225 커넥트(connect) 메시지를 전송해 연결 설정이 수락됐음을 알린다.
9. H.245 제어채널이 단말 1과 단말 2에 성립된다. 단말 1은 H.245 TerminalCapabilitySet 메시지를 전송하고 단말 2와 성능(Capability)에 대한 정보를 교환한다.
10. 단말 2는 단말1의 성능 정보가 확인됐음을 Terminal CapabilitySetAck를 통해 알린다.
11. 단말 2는 단말 1에게 TerminalCapabilitySet을 전송해 자신의 성능 정보를 전송한다.
12. 단말 1 역시 동일하게 TerminalCapabilitySetAck를 전송해 단말 2의 성능 정보가 확인됐음을 알린다.
13. 단말 1은 단말 2에 RTCP 채널의 전송주소가 포함돼 있는 openLogicalChannel 메시지를 전송해 미디어 채널을 만든다.
14. 단말 2는 RTP 전송주소가 포함된 H.245 openLogical ChannelAck 메시지를 통해 단말 1에게 단방향의 논리 채널이 성립됐음을 알린다.
15. 단말 2는 RTCP 채널의 전송주소가 포함된 H.245 open LogicalChannel 메시지를 전송해 단말 1에 미디어 채널이 성립됐음을 통지한다.
16. 단말 1은 단말 2로 openLogicalChannelAck 메시지를 보냄으로써 단말 2로부터 단말 1까지의 단방향 논리 채널이 형성됐음을 통보한다. H.245 openLogicalChannelAck 메시지에는 단말 1의 RTP 주소가 포함돼 있으며, 이를 통해 양방향 미디어 실시간 통신이 가능하게 된다.
17. 단말 1은 RTP로 인코딩된 미디어 스트림을 단말 2로 전송한다.
18. 단말 2은 RTP로 인코딩된 미디어 스트림을 단말 1로 전송한다.
19. 단말 1은 RTCP 메시지를 단말 2로 전송한다.
20. 단말 2는 RTCP 메시지를 단말 1로 전송한다.
21. 단말 2가 H.245 EndSessionCommand 메시지를 단말 1로 전송해 연결 종료를 시도한다.
22. 단말 1은 H.245 EndSessionCommand 메시지를 단말 2로 전송함으로써 통신 종료를 준비한다.
23. 단말 2는 H.225 릴리즈 컴플릿(release complete) 메시지를 단말 1에 전송함으로써 콜을 종료한다.
24. 단말 1과 단말 2는 게이트키퍼에 RAS DRQ(Disengage ReQuest) 메시지를 전송해 게이트키퍼와의 접속을 해제한다.
25. 게이트키퍼는 단말 1과 단말 2에 DCF(Disengage ConFirmed) 메시지를 보냄으로써 접속해제를 알린다.
2. SIP
1) 개요
SIP(Session Initiation Protocol)는 인터넷을 포함하는 패킷 네트워크 상에서 통신하고자 하는 단말들을 식별하고 위치를 파악하며, 그들 상호간에 멀티미디어 통신 세션을 생성하거나 삭제, 변경하기 위한 절차를 명시한 애플리케이션 계층의 시그널링(signaling) 프로토콜이다. 또한 네트워크 전송 프로토콜과 미디어에 완벽하게 독립적이고 콘텐츠에 상관없이 어떻게 단말기의 연결을 생성하거나 변경 혹은 종료하는지를 정의한다.
SIP의 출현은 인터넷을 이용한 통신 서비스 시장에 큰 파급효과를 가져왔다. 기존의 VoIP 시스템은 대부분 ITU-T가 표준으로 채택한 H.323 프로토콜을 기반으로 구현돼 있다. H.323은 원래 패킷 교환 방식의 랜 망에서 다자간 음성, 화상, 데이터 통신을 가능케 하기 위해 개발된 기술 방식이므로 광대역 네트워크와 대규모 사용자를 지원하는 데 있어서는 기본적으로 한계점을 가지고 있었던 게 사실이다. VoIP 관련 시장 규모가 크게 성장함으로 인해 인터넷 전화 기술이 시장성 있는 기술로 각광을 받으면서 인터넷 상에서 양자간/다자간 통신을 하기 위한 시그널링 프로토콜인 SIP가 기존의 H.323을 대체하는 기술로 주목을 받게 됐다.
SIP는 MGCP(the Media Gateway Control Protocol)의 업그레이드된 프로토콜이다. MGCP는 PSTN의 음성 신호를 IP 데이터 패킷으로 변환시키는 프로토콜이었지만 확장성이 부족하고 음성신호만을 위한 표준이었으며 시그널링이 복잡한 프로토콜이었다. 특히 SIP는 MGCP의 단점을 해결한 프로토콜로 멀티미디어에 특화된 새로운 환경을 제시했다.
SIP는 HTTP와 매우 유사한 메시지 타입을 유지함으로써 개발자들이 자바 같은 대중적인 프로그래밍 언어를 통해 좀더 쉽고 빠르게 애플리케이션을 개발할 수 있게 한다. 또한 통신 사업자들에게도 CID(Caller ID) 서비스, 콜 대기(call waiting) 서비스 등 PSTN의 지능망에서 제공되는 여러 가지 프리미엄 서비스들을 동일하게 제공할 수 있다.
이렇듯 SIP의 유연한 확장성은 SIP를 VoIP 음성서비스의 새로운 표준으로 만드는데 기여했으며, 차세대 VoIP 프로토콜의 지배적인 표준으로서 입지를 굳혀나가고 있다. 또한 3G 협회는 SIP를 차세대 무선통신망의 세션 제어 메커니즘으로 선택했으며, 마이크로소프트는 윈도 운영체제, MSN 메신저 및 기타 애플리케이션의 실시간 통신을 위한 기본 프로토콜로 탑재할 것을 발표했다.
2) 주요 특징
SIP의 주요 특징은 세션을 성립시킬 때 세션의 타입을 정의하지 않고 어떻게 운영해야 될 지만 기술한다는 점이다. 이러한 유연성으로 인해 SIP는 VoIP 음성 서비스뿐만 아니라 온라인 게임, 컨퍼런싱 등의 많은 애플리케이션에 사용될 수 있다. 또한 SIP 메시지는 텍스트 기반으로 구성돼 있으므로, 해석과 디버그가 용이하며 새로운 서비스를 쉽고 간편하게 프로그래밍할 수 있다.
SIP는 MIME(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) 타입 및 DNS(Domain Name System), RTP(Real-Time Transport Protocol), RTSP(Real Time Streaming Protocol) 등 현존하는 프로토콜을 재사용하기 때문에 더욱 최적화된 세션 설정이 가능하다. 또한 SIP를 지원하기 위한 또 다른 서비스를 정의할 필요가 없다.
SIP는 쉽게 확장할 수 있으며, 현존 네트워크 구조를 변경시키지 않고 새로운 애플리케이션 서비스가 가능하다. 이전 버전의 SIP 장비는 새로운 버전의 SIP를 기반으로 한 장비들과 충돌하지 않는다. 새로운 버전의 SIP는 구 SIP의 헤더 및 메소드를 무시하기 때문이다. 또한 전송계층에 독립적이기 때문에 ATM 망에서의 IP계층 위에서도 운용가능하며, 하부계층에 상관없이 UDP, TCP를 통한 전송이 가능하다.
3) 구성 요소
SIP 세션을 성립시키기 위해서는 SIP 유저 에이전트(UA), SIP 프록시 서버, SIP 레지스트라 서버(Registrar servers), 그리고 SIP 리다이렉트 서버가 필요하다. SIP 유저 에이전트는 휴대폰, PC 및 기타 SIP 사용 가능한 단말기를 통칭한다. SIP 세션을 설정하고 운영하며, SIP 연결을 요청한 단말을 클라이언트(UAC), 연결에 응답한 단말을 서버(UAS)로 분류한다.
SIP 레지스트라 서버는 데이터베이스, 도메인(domain)에 있는 모든 UA의 장소정보 및 IP 주소정보를 저장해 SIP 프록시 서버의 질의에 응답한다. SIP 프록시 서버는 SIP UA에서 요청하는 세션을 수락하고, 응답하는 UA의 주소정보를 SIP 레지스트라 서버에 질의하는 역할을 담당한다. 같은 도메인 상에 서버(UAS)가 존재시 세션 요청을 서버(UAS)에게 보내며, 서버(UAS)가 다른 도메인에 있을 경우에는 다른 도메인의 프록시 서버에 세션 요청을 전송한다.
SIP 리다이렉트 서버는 다른 도메인에 존재하는 SIP 세션 요청에 대해서 현존 도메인 내에 존재하는 SIP 프록시 서버가 직접적인 설정을 가능하게 한다.
4) 주소 및 메시지
SIP 주소형식은 기본적으로 이메일과 매우 유사한 sip:user_id@domain_name의 형식을 가지게 되며, 만약 DNS가 존재하지 않으면 domain_name 부분을 IP 주소로 대체할 수 있다. user_id 부분은 부여된 전화번호로 대체가 가능하다. 즉 sip:031xxxxxxx@62.xx.xx.xx;user=phone는 sip:user_id@domain_name와 SIP에서 동일한 주소를 나타낸다.
메시지는 텍스트 기반이며 전술한 바와 같이 HTTP를 재사용한다. 따라서 웹 서핑에서 발생되는 메시지와 동일성을 가진다. 크게 SIP 메시지는 클라이언트에서 요청하는 리퀘스트(Request)와 서버 응답인 리스펀스(Response)로 나눠진다. 메시지 타입은 다음과 같다.
5) 콜 셋업 과정
같은 도메인 내에 UAS가 존재할 경우에는 클라이언트(UAC) A와 서버(UAS) B는 IP 주소 및 수신가능 여부를 SIP 프록시 서버에 자동적으로 전송한다. 클라이언트(UAC) A가 콜을 설정 시 SIP 프록시 서버에 단말 B에 대한 통신 요구를 전송하면, SIP 프록시 서버는 SIP 레지스트라 서버에 주소 정보 요청을 통해 서버(UAS)의 IP 주소를 전송받는다. 그 후 SIP 프록시 서버는 클라이어트(UAC)의 인바이트(invite) 메시지를 서버(UAS)에 재전송하며 SDP에서 정의하는 클라이언트(UAC)가 세션에 사용하는 매체(음성, 영상 등)에 대한 정보가 포함된다.
서버(UAS)는 SIP 프록시 서버에게 콜 셋업이 가능한지와 수신 가능 여부를 회신하며, 마지막으로 SIP 프록시 서버가 클라이언트(UAC)에 정보를 전송함으로써 서버(UAS)와 클라이언트(UAC)간의 SIP 세션이 성립되는 절차를 따른다. 그 후 RTP를 이용한 통신이 P2P(Point-to-Point)로 이뤄지면서 실제적인 VoIP 음성서비스가 시작되게 된다.
만약 클라이언트(UAC)와 서버(UAS)가 동일한 도메인에 존재하지 않으면 절차가 달라진다. 클라이언트(UAS) A가 콜 설정시 SIP 프록서 서버에 단말 B에 대한 통신 요구를 전송하게 되는 것은 앞선 경우와 동일하나, SIP 프록시 서버가 도메인 B에 직접적으로 접속돼 있지 않으므로 같은 도메인 내의 SIP 레지스트라 서버는 도메인 B의 SIP 프록시 서버 주소를 전송한다. 도메인 A에 존재하는 프록시 서버는 도메인 B에 존재하는 프록시 서버에 콜을 넘겨주게 되며, 도메인 B에 존재하는 프록시 서버는 역시 같은 도메인 내에 존재하는 레지스트라 서버에 서버(UAS)의 주소를 질의한다.
도메인 B에 존재하는 레지스트라 서버는 서버(UAS)의 주소정보를 프록시 서버 B에 전송하고 서버(UAS) B는 프록시 서버 B에 응답 메시지를 전송한다. 이후 프록시 서버 B는 프록시 서버 A에 응답하며, 프록시 서버 A는 다시 클라이언트(UAC)에 응답 메시지를 전송하게 됨으로써 콜 셋업이 마무리된다.
3. H.323과 SIP 비교
VoIP 시스템에 적용되는 대표적인 두 가지 프로토콜인 H.323과 SIP는 다음과 같은 장단점을 가진다. 첫째로 H.323에 비해 SIP는 간편하고 간결한 장점으로 인해 새로운 기능 및 부가서비스 제공이 H.323에 비해 용이하다. 둘째로 H.323은 복잡한 프로토콜 구조로 인해 지연시간 증가와 과다한 자원요구 등의 단점을 가지고 있다. 마지막으로 SIP는 H.323보다 간단한 구조로 인해 통신사용자간 충분한 정보를 교환할 수 없다.
<표 2>와 같이 H.323은 좀더 현재의 PSTN망에, SIP는 인터넷 망에 각각 초점을 맞춰 발전했다. SIP가 지배적인 VoIP 시스템의 운용 프로토콜이 될 것으로 예상되지만, 그 과정에서 H.323의 장점을 적극 수용할 것으로 보인다.
이번 호는 VoIP 시스템을 구성하는 대표적인 프로토콜인 SIP와 H.323에 대해 알아봤다. 다음호에서는 VoIP 시스템의 네트워크 구조를 알아봄으로써 VoIP 시스템의 전체적인 구조를 파악해 보자.
'Network > Netowrk_network' 카테고리의 다른 글
| ENUM (0) | 2009.01.18 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 Header (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| VoIP 관련 표준 문서 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| IP헤더 (0) | 2009.01.18 |
| IP Header 와 IP 서비스의 특징 (0) | 2009.01.18 |

 1-5testdata.xls
1-5testdata.xls 업스트림과다운스트림간불공평성문제를개선시키기위한알고리즘.doc
업스트림과다운스트림간불공평성문제를개선시키기위한알고리즘.doc source.zip
source.zip ns2.hwp
ns2.hwp